Figure 3. Cellular response to CDK4/6 inhibition in combination with chemotherapy.
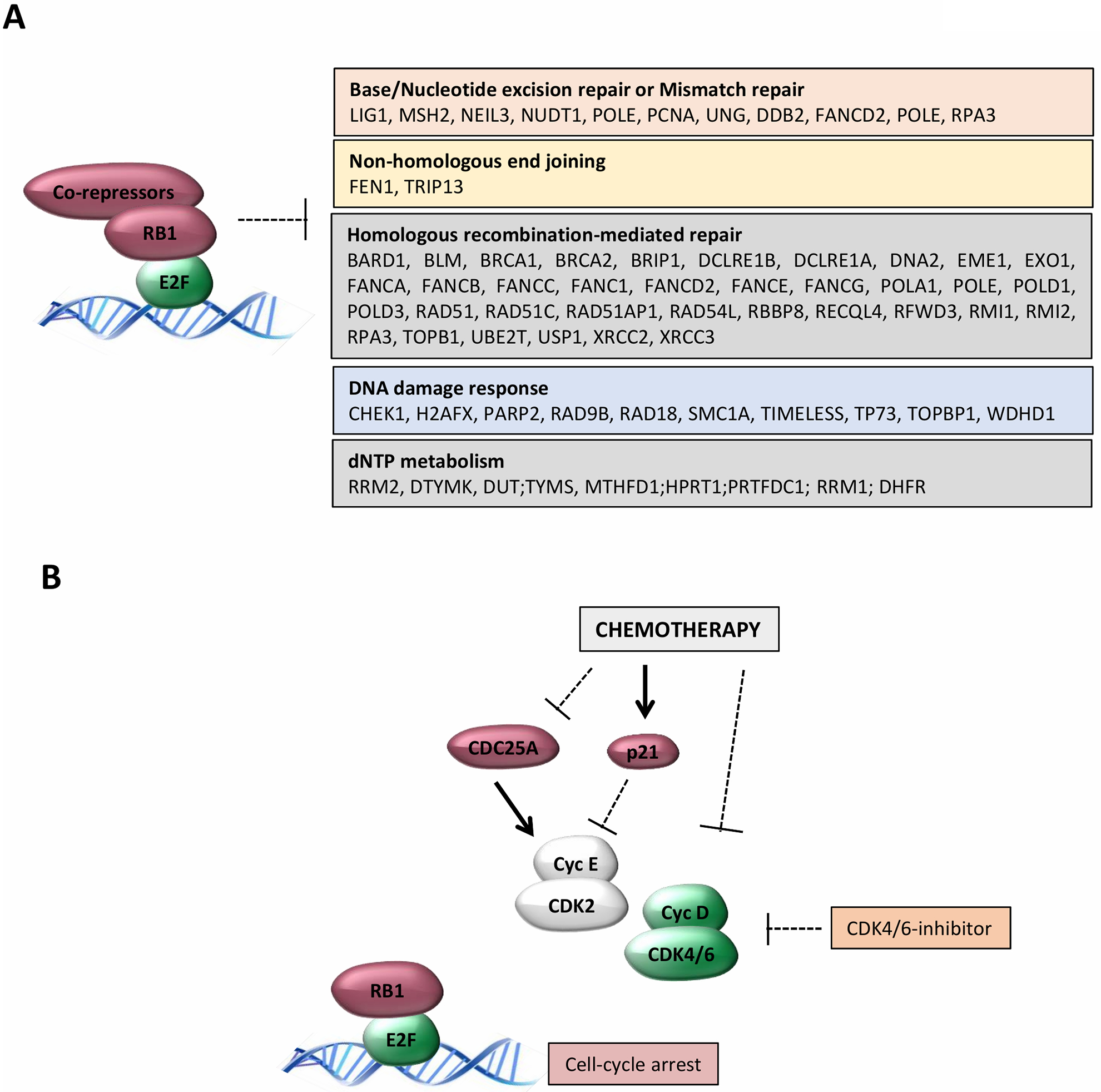
(A) Downstream from the activation of the RB-pathway are the repression of multiple genes involved in different pathways that could impinge on different features of response to distinct chemotherapeutic agents. (B) There are multiple mechanisms through which chemotherapy impinges on the activity of CDK2 and CDK4/6 complexes that would be expected to enhance the efficacy of pharmacological CDK4/6 inhibitors. For example, CDC25A is rapidly degraded or the CDK2-inhibitor P21CIP1 is rapidly induced as a specific response to chemotherapy. Conversely, degradation of cyclin D1 and inhibition of CDK4/6 complexes is a consequence of different chemotherapy agents that induce S-phase block.
