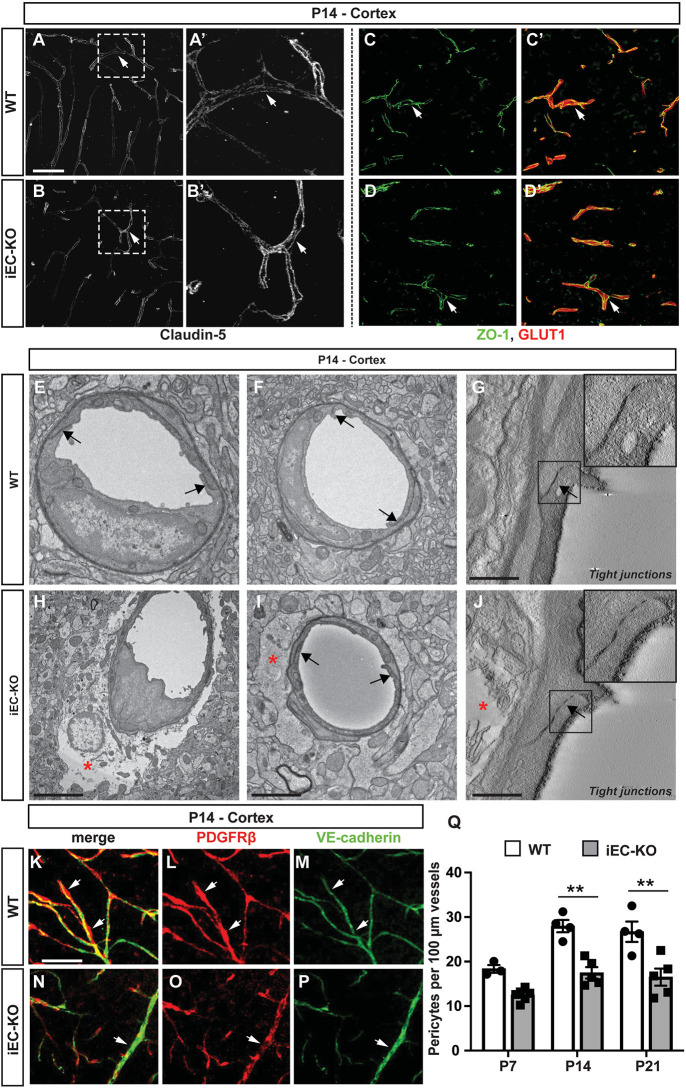
Fig. 3.
Ultrastructural integrity of tight junctions is maintained in Fgfbp1iEC-KO mice. (A-D′) Immunofluorescence for claudin 5 (A-B′), ZO-1 (green) and Glut1 (red) (C-D′) in the cortex of WT (A,A′,C,C′) or Fgfbp1iEC-KO (B,B′,D,D′) P14 pups. The expression and localization of claudin 5 and ZO-1 is similar between the two genotypes. (E-J) TEM analysis of the cortical capillaries from WT (E-G) and Fgfbp1iEC-KO (H-J) mice at P14 (60 nm thick sections, n=3 animals/group). There is no difference in tight junction morphology (E-J, black arrows and insets in G and J) between the two genotypes. However, a subset of capillaries in Fgfbp1iEC-KO show abnormal astrocyte endfeet swelling (E-J, red asterisk). (K-P) Analysis of pericytes in the cortex of WT (K-M) and Fgfbp1iEC-KO (N-P) P14 pups. Brain sections (100 µm thick) were stained for PDGFRβ (red) and VE-cadherin (green). (Q) Quantification of the pericyte number in WT and Fgfbp1iEC-KO at P7, P14 and P21 cortices. Each dot represents the average of at least three confocal acquisitions from a single animal. There is reduced pericyte number in Fgfbp1iEC-KO P14 and P21 pups compared with WT pups. Data are mean±s.e.m. **P<0.01; Student's t-test. Scale bars: 50 µm in A-D′,K-P; 1 µm in E,F,H,I; 250 nm in G,J.