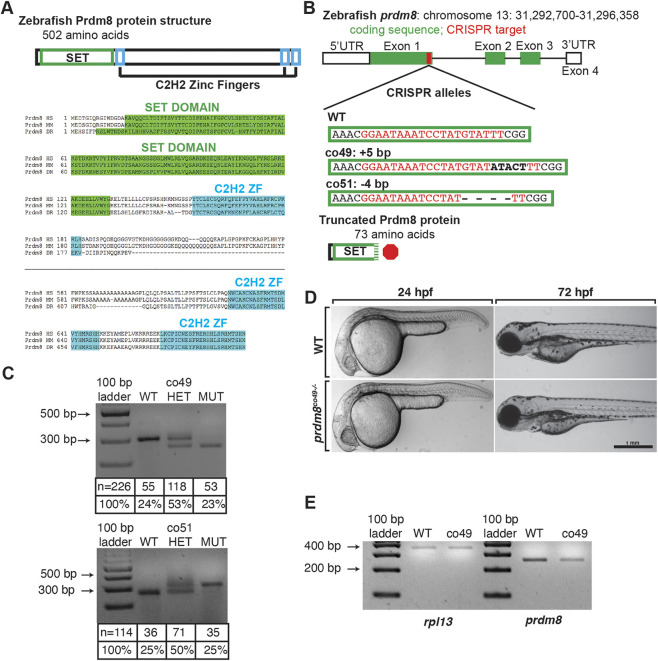
Fig. 3.
Generation and characterization of prdm8 loss-of-function mutations. (A) Zebrafish Prdm8 protein structure is depicted as an empty black box with the SET domain highlighted in green and the C2H2 zinc-finger domains in blue. Alignment of Prdm8 amino acid sequences from human (HS), mouse (MM), and zebrafish (DR). Conserved SET domain and C2H2 zinc-finger domains are shown as green or blue boxes, respectively. (B) Schematic representing prdm8 gene structure. The sequence targeted for CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis is marked by a red line in exon 1. The wild-type sequence CRISPR target sequence is shown below in red text and the co49 insertion and co51 deletion are shown in bold or dashes, respectively. Both mutations are predicted to produce 73 amino acid proteins truncated at the C-terminal end of the SET domain. (C) Images of agarose gels showing prdm8 DNA fragmentation following dCAPS genotyping of homozygous wild-type (WT), heterozygous and homozygous mutant embryos with sample genotype frequencies. (D) Representative images of living 24 and 72 hpf wild-type and prdm8co49−/− embryos. (E) Image of RT-PCR gel, showing decreased expression of prdm8 mRNA in prdm8 mutant embryos compared with control, with no difference in expression of the control transcript rpl13.