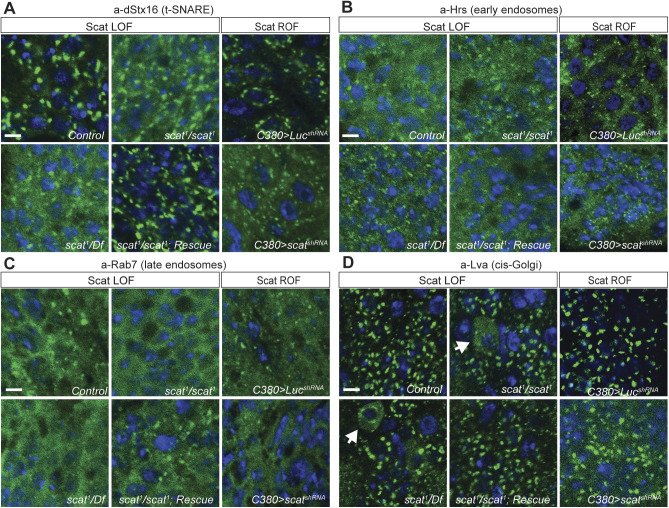
Fig. 4.
scat mutant MNs have defects in Syntaxin-16 localization and cis-Golgi integrity. (A) Localization of Syntaxin-16 to the TGN is disrupted in scat1 mutants. Images shown are single focal planes. Ventral ganglia from wandering third instar larvae from controls, scat1 homozygotes, scat1/Df(2L)Exel8022, and the scat1/scat1; scat-HA:scat/scat-HA:scat rescue lines were stained with an antibody targeting (A) dStx16 (green) and DAPI to visualize nuclei (blue). dStx16 staining is significantly more diffuse (but still clearly punctate) in scat1 mutants compared to controls. The scat1 mutant phenotype is rescued by the introduction of the scat-HA:scat transgene. Similar results were observed in C380>scat shRNA MNs. (B) EEs are not affected in scat1 mutants. The indicated genotypes were stained with an antibody targeting the EE- and multivesicular body-associated protein, Hrs (green) and DAPI (blue). (C) LEs are not affected in scat mutants. The indicated genotypes have been stained with an antibody targeting Rab7 (green) and DAPI (blue). (D) Localization of the cis-Golgi marker, Lva is partially disrupted in the cell body of some scat mutant and motor neurons (arrows). The indicated genotypes have been stained with an antibody targeting Lva (green) and DAPI (blue). This phenotype is never observed in control or rescue larvae. More global effects are observed in C380>scat shRNA MNs. Scale bars: 2.5 µm.