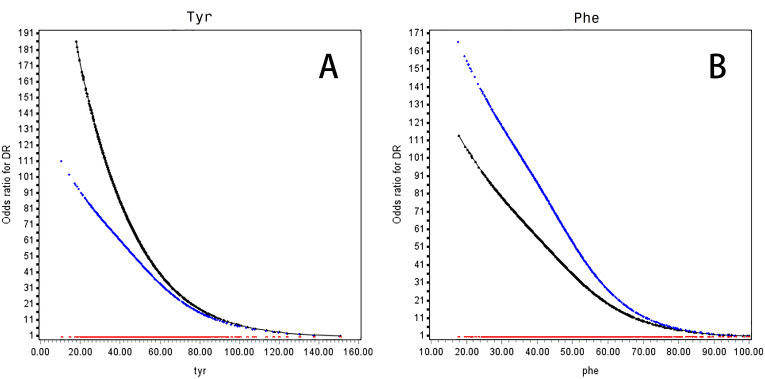
Figure 1.
OR curves of Tyr (A) and Phe (B) for DR in Chinese patients with T2D. The black curve was derived from univariable analysis, and the blue curve was derived from multivariate analysis that adjusted for age, sex, body mass index (<18.5, 18.5–24.0, 24.0–28.0 and >28.0 kg/m2), duration of diabetes, systolic blood pressure, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (<1.0 mmol/L in men or <1.3 mmol/L in women, ≥1 mmol/L in men or ≥1.3 mmol/L in women, lack), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (<2.6 and ≥2.6 mmol/L, lack), HbA1c (<7%, 7%~8%, and ≥8%, lack), triglyceride (<1.7 and ≥1.7 mmol/L, lack), diabetic nephropathy, antidiabetic drugs, lipid-lowering drugs and antihypertensive drugs. The red curve stands for the reference level (ie, the OR for DR was 1). The concentration of Phe was coded to 45.34 μmol/L (mean) if Phe≥100.00 μmol/L. Missing values of HbA1c and lipids were presented as one category. DR, diabetic retinopathy; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; Phe, phenylalanine; T2D, type 2 diabetes; Tyr, tyrosine.