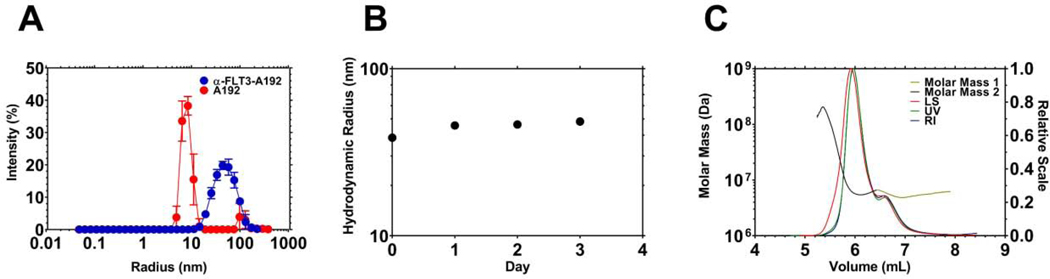
Figure 2. Recombinant α-FLT3-A192 fusions form stable nanoparticles.
A) The hydrodynamic radius (Rh) of recombinant α-FLT3-A192 was measured using dynamic light scattering (DLS) at 37 °C. While A192 has a size consistent with the molecular weight of a free polymer, α-FLT3-A192 formed a larger and more polydisperse population of nanoparticles. B) Nanoparticle stability at 37 °C was measured with DLS over three days. The Rh did not change substantially, which suggests the nanoparticles remain stable colloids. C) Size exclusion chromatography multi-angle light scattering (SEC-MALS) was employed to measure the absolute molar mass and the radius of gyration of the nanoparticles. Two peaks were observed, and their average molecular weights were 6.4×106 Da and 5.6×106 Da for major peak 1, minor peak 2 respectively. Based on the expected molecular weight of the expressed fusion protein, these nanoparticles are composed of ~sixty FLT3-A192 molecules. These nanoparticles have Rg/Rh ratio = 1.1, which is consistent with an extended nanoworm shape.