Fig. 4.
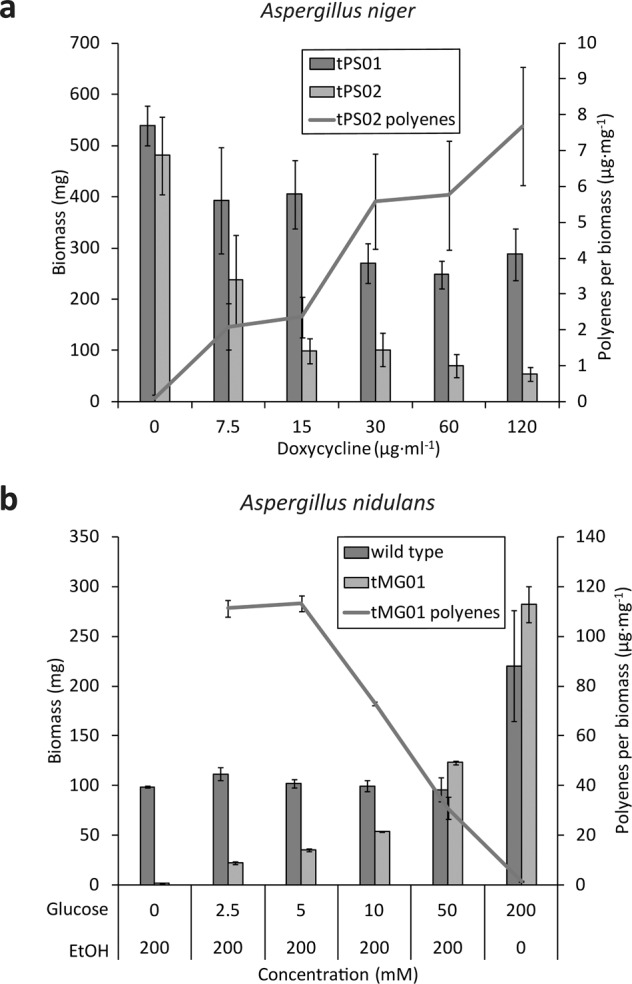
Antifungal activity of laetiporic acids produced in situ by Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal dry biomass (in mg) was determined for A. niger tPS02 (lpaA-expressing) and tPS01 (vector control) (a) or A. nidulans tMG01 (lpaA-expressing) and FGSC A4 wildtype strain (b), respectively. Polyene production was induced by adding doxycycline (7.5–120 µg ml−1) in A. niger and repressed by d-glucose (2.5–50 mM) in A. nidulans. Cultures without inducer, i.e., doxycycline for A. niger or ethanol in A. nidulans, served as negative controls. Intracellular polyene concentration is given in µg per mg dry fungal biomass. Polyene production is increased 15-fold in A. nidulans, compared to A. niger, resulting in a more intense coloration and an antifungal effect (no growth under non-repressing conditions). Hence, polyene content could not be determined under this condition. Bars indicate the standard deviation (n = 3)
