Fig. 3.
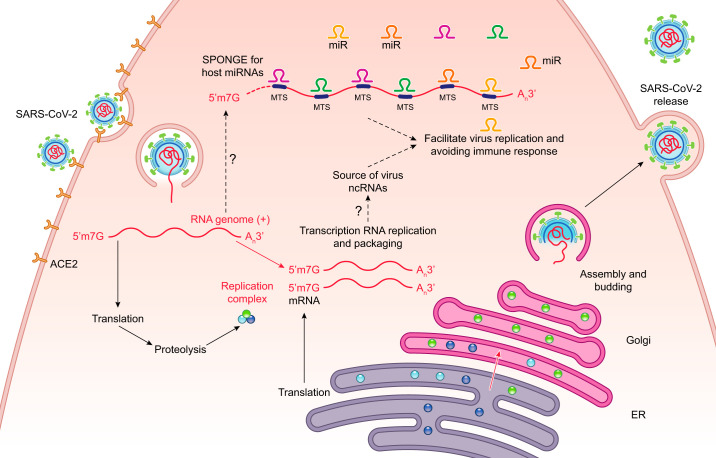
The hypothesis is that severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) regulates cellular responses through depletion of specific host microRNAs (miRNAs). The SARS-CoV-2 uptake and replication cycle is illustrated and our model is that noncoding viral RNAs serve as sponges for the host miRNAs and this accomplishes two goals. First, it disrupts normal cellular homeostasis by upregulating specific host mRNA levels that are normally controlled by host miRNAs. And second, by downregulating certain host miRNAs, the virus enhances its own viral replication cycle and also attenuates immune responses. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; MTS, microRNA target sites.