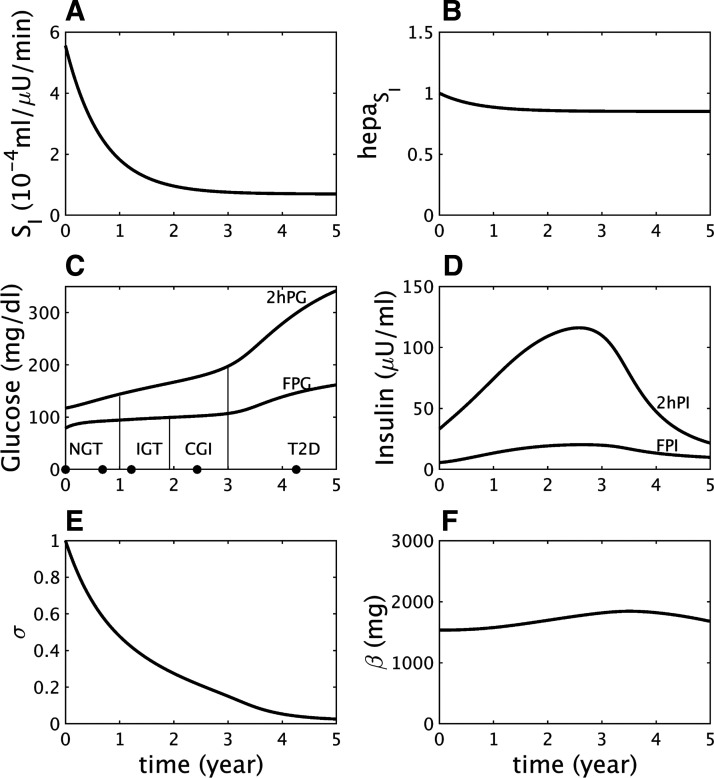
Fig. 1.
Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT)-first pathway to diabetes. A: assumed severe decline in peripheral insulin sensitivity (SI). B: assumed mild decline in hepatic insulin sensitivity (). C: simulated longitudinal changes based on the assumptions in A and B in fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and 2-h glucose (2hPG) during oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTTs) performed at each time point. The virtual subject experiences first high 2 h glucose (IGT), then high fasting glucose [combined glucose impairment (CGI)], and finally crosses the 2hPG threshold for type 2 diabetes (T2D). NGT, normal glucose tolerance. D: simulated longitudinal changes in fasting plasma insulin (FPI) and 2 h insulin (2hPI) during the OGTTs. Insulin increases early on but decreases later. E: the component of β-cell function represented by σ decreases progressively throughout. F: the β-cell mass, β, first increases during prediabetes and then decreases after diabetes onset.