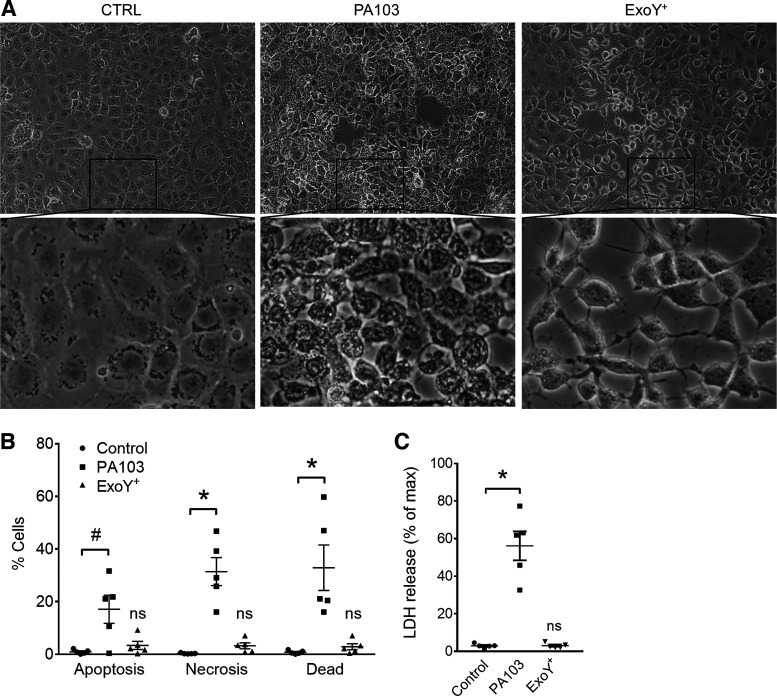
Fig. 1.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme Y (ExoY) causes pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell (PMVEC) rounding independent of cell death. A: PMVECs were treated with vehicle control (CTRL; left) or inoculated with P. aeruginosa strain PA103 (middle) or ExoY+ (right). Monolayer images were taken at 4 h (PA103) or 6 h (CTRL and ExoY+) postinoculation. B: infected PMVECs were stained with both annexin V (AV) and propidium iodide (PI). Cell death was analyzed by flow cytometry. “Apoptosis” refers to cells that stained positive for AV alone, “necrosis” refers to cells that stained positive for PI alone, and “dead” refers to cells that stained positive for both AV and PI. Each data point represents 1 experiment performed in duplicate. Data were analyzed by 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. Interaction not significant (P = 0.1615), row factor (cell death type) not significant (P = 0.2359), column factor (infection condition) significant, P < 0.0001. C: cell culture supernatants from infected PMVECs were analyzed for lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release. Each data point represents 1 experiment performed in duplicate. Data were analyzed by ordinary 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple-comparison test. ANOVA, P < 0.0001. #P = 0.0158; *P < 0.0001. NS, not significantly different from control, n = 5.