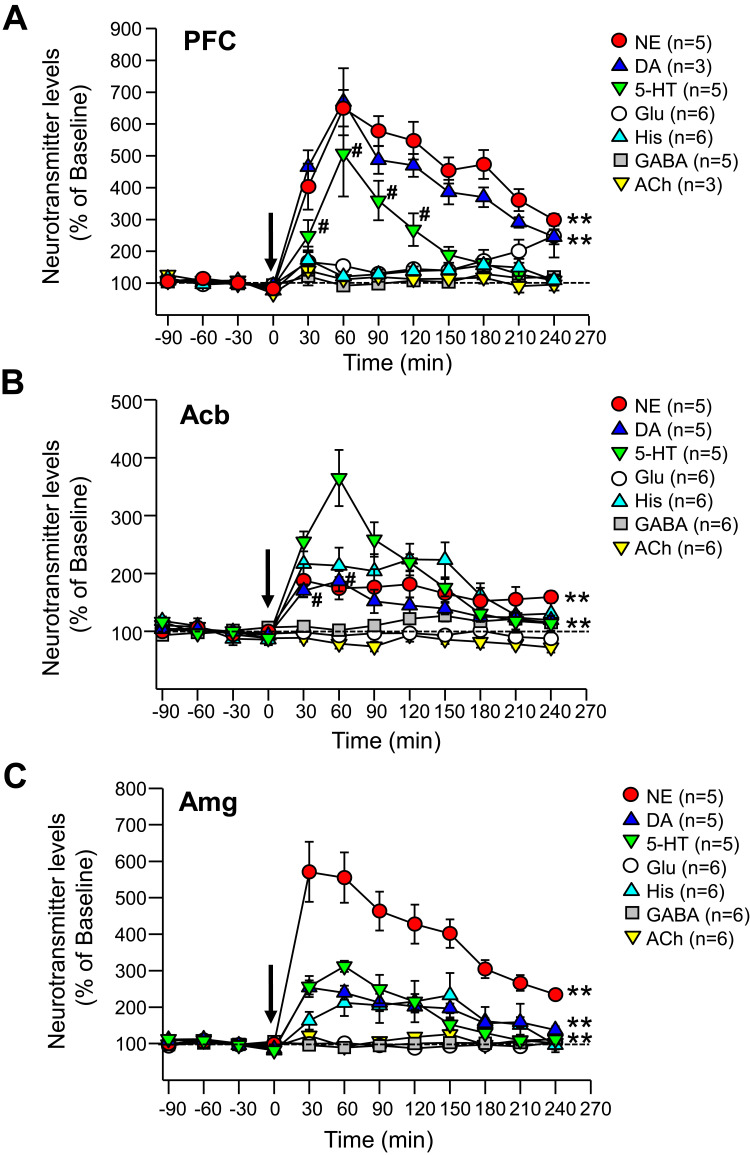
Figure 3.
Effects of viloxazine on neurotransmitter levels in the PFC, Acb, and Amg of freely moving rats. Administration of viloxazine (50 mg/kg, IP) at time 0 is indicated by the arrow. (A) In the PFC, viloxazine significantly increased extracellular levels of NE and DA throughout the 4 h period (**p < 0.001, Dunnett’s post hoc test) and 5-HT from 30 to 120 minutes (#p < 0.05 Dunnett’s post hoc test) in comparison to vehicle treated groups. (B) In the Acb, extracellular levels of 5-HT and NE increased throughout the 4 h period (**p < 0.001, Dunnett’s post hoc test) and DA from 30 to 60 min (#p < 0.05, Dunnett’s post hoc test). (C) In the Amg, extracellular levels of 5-HT, NE, and DA increased throughout the 4 h period (**p < 0.001, Dunnett’s post hoc test). Measured neurotransmitter levels (mean ± SEM) are reported as the percent of pre-treatment baseline. The statistical post-hoc analyses of vehicle vs viloxazine at each time point (T = 0 to T = 240) and significant interactions (two-way ANOVA with p<0.05) are presented in the Table 2.
Abbreviations: 5-HT, serotonin; Acb, nucleus accumbens; ACh, acetylcholine; Amg, amygdala; ANOVA, analysis of variance; DA, dopamine; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; Glu, glutamate; His, histamine; IP, intraperitoneal; NE, norepinephrine; PFC, prefrontal cortex; SEM, standard error of the mean.