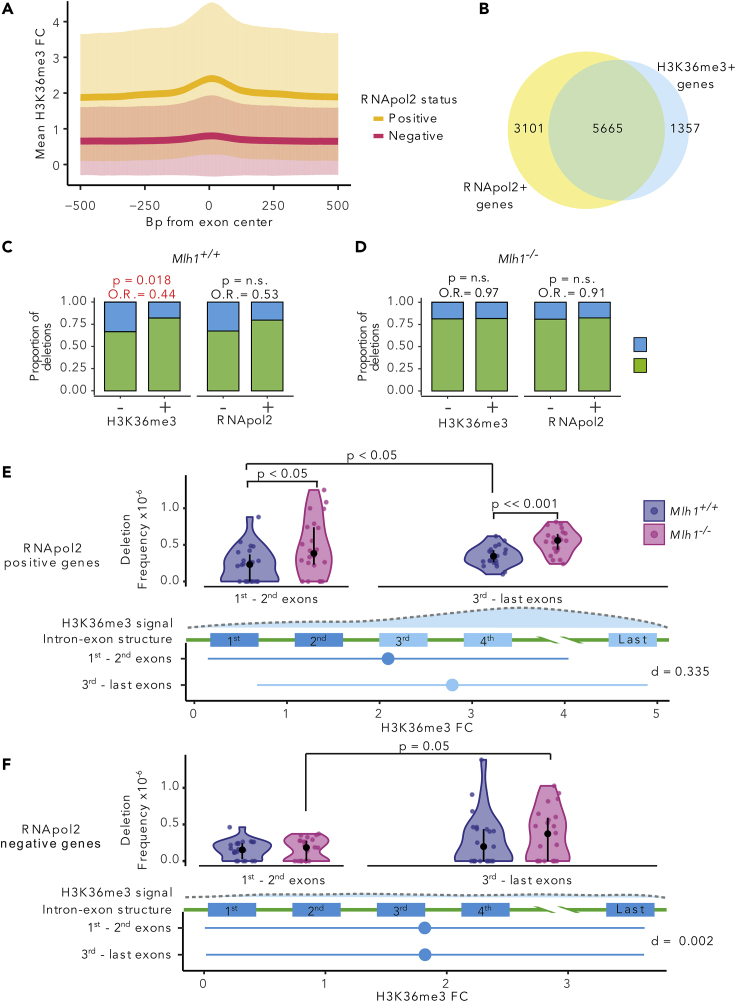
Figure 5.
H3K36me3 Reduces the Amount of MMR-Dependent Mutations in Exons
(A) H3K36me3 fold change (FC) (mean ± SD) in 1,000-bp window around exon centers in RNApol2-positive and -negative genes.
(B) Venn diagram of RNApol2-positive (+) and H3K36me3-positive (+) gene counts. Proportions of small deletions in genes positive or negative for H3K36me3 and RNApol2 in (C) Mlh1+/+ and (D) Mlh1−/− cells. Coding regions in genes positive for H3K36me3 have fewer deletions relative to H3K36me3-negative genes in Mlh1+/+ cells (p = 0.018, OR = 0.44, two-tailed Fisher's exact test), but not in Mlh1−/− cells. Deletion frequencies in the first to second exons (5′ exons) and the third to last exons (3′ exons) in RNApol2 (E) -positive and (F) -negative genes. In RNApol2-positive genes, Mlh1−/− cells have higher deletion frequency especially in the third to last exons (high H3K36me3) than Mlh1+/+ cells, and to lesser degree, in the first to second exons (low H3K36me3). The first panel shows the deletion frequencies in Mlh1+/+ and Mlh1−/− cells. data is shown as median and interquartile range together with kernel probability density and individual datapoints See also Figures S5 and S6. The second panel shows a schematic of H3K36me3 enrichment along a gene. The third panel shows a schematic of a gene structure. The fourth panel shows H3K36me3 signal as mean ± SD of FC in the first to second exons and third to last exons together with effect size as Cohen's d with Bessel's correction. Deletion frequencies were tested using two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test.