Figure 1.
Identification of Phosphorylated Residues of BYSMV P by Mass Spectrometry.
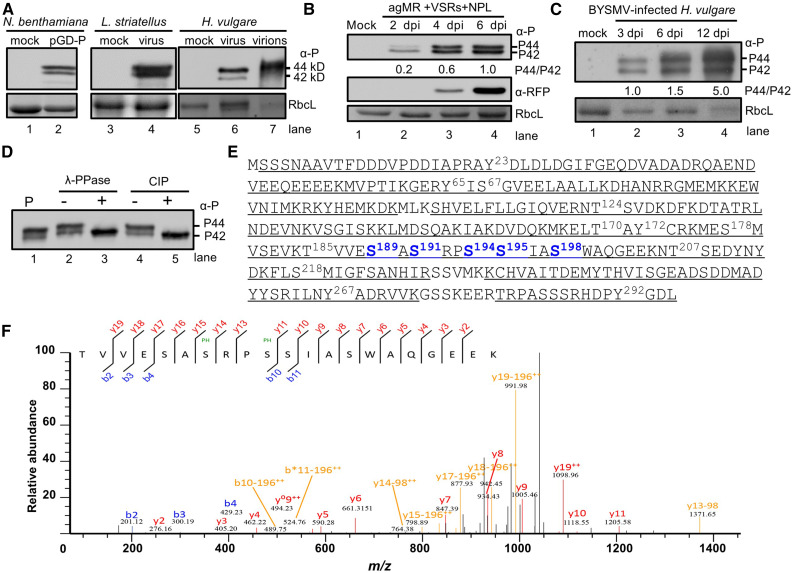
(A) Immunoblot analysis showing two forms of the P protein expressed in N. benthamiana, L. striatellus, and H. vulgare, and purified virions, using specific antibodies against the P protein. Note the presence of two BYSMV P protein bands (P42 and P44) with molecular masses of 42 and 44 kD in gels.
(B) Accumulation of BYSMV P and RFP in agMR-inoculated N. benthamiana leaves at 2, 4, and 6 dpi. Total protein extracts from agMR-inoculated N. benthamiana leaves were probed with anti-P and anti-RFP antibodies. The P44:P42 ratios were calculated from band intensities.
(C) Accumulation of BYSMV P in BYSMV-infected H. vulgare plants at 3, 6, and 12 dpi. Coomassie Brilliant blue (CBB) staining of Rubisco complex large subunit (RbcL) was used as protein loading controls in (A) to (C).
(D) Treatment of BYSMV P proteins with phosphatase. P-Flag proteins were isolated from N. benthamiana leaves infiltrated with the plasmid pMDC32-P by immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag beads. P-Flag proteins were treated with lambda protein phosphatase (λ-PPase) or CIP. Mock treatment (–) was incubated with buffer without phosphatases.
(E) Mass spectrometric identification of BYSMV protein phosphorylation sites. Underlined peptides (bold) were identified by mass spectrometry. The bold and numbered residues represent phosphorylation sites. Highly phosphorylated Ser residues of the BYSMV P protein SR motif are shown in blue.
(F) MS/MS spectrum of the peptide 185TVVESASRPSSIASWAQGEEK205 containing the Ser-191 and Ser-194 phosphorylated residues. The b and y ions are highlighted in the sequence and corresponding labels in the spectrum.