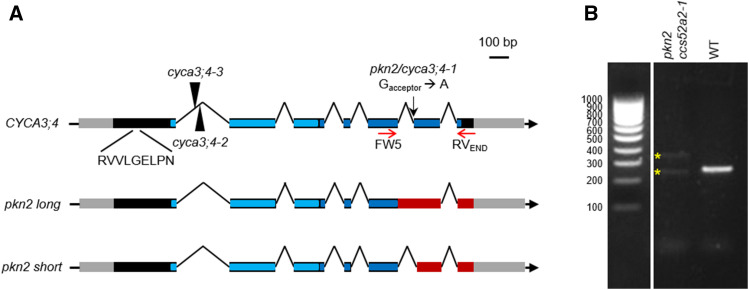
Figure 2.
The CYCA3;4 Gene Structure.
(A) The gene structure of the wild-type CYCA3;4 gene, showing the location of the EMS mutation (black arrow), T-DNA insertions (arrowheads), and D-box sequence. The two splice variants created through the pkn2 mutation are shown below. The gray and black boxes represent the untranslated regions and the coding sequences, respectively, while the lines represent the intergenic sequences and introns. The predicted N- and C-terminal cyclin folds are indicated in light and dark blue, respectively. In the mutant variants, the out-of-frame sequences are indicated in red.
(B) RT-PCR on whole-seedling cDNA of pkn2 ccs52a2-1 and wild type (WT; Col-0) using CYCA3;4 primers FW5 and RVEND (represented by red arrows in [A]), and, whereas only one amplicon was detected for the WT, two distinct amplicons were detected for the revertant (yellow stars), representing two newly created splice variants.