Figure 5.
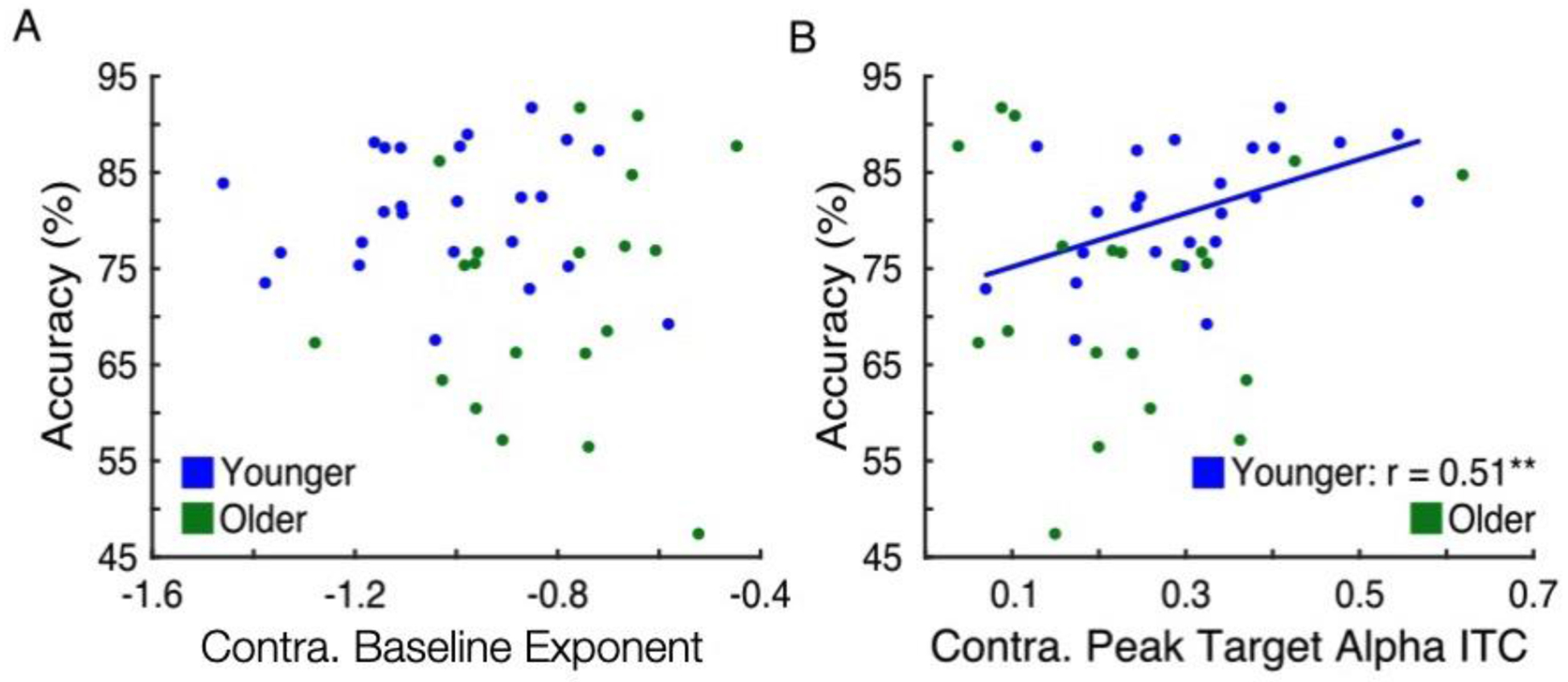
Baseline noise was not correlated with behavioral accuracy, but decreased response variability was associated with higher accuracy in younger but not older adults. (A) Accuracy across all cue conditions versus contralateral baseline spectral exponent in younger (blue) and older (green) adults. No relationship was found. (B) Accuracy versus contralateral peak target-evoked alpha ITC in younger (blue) and older (green) adults, with best-fit line for younger adults. In younger but not older adults, higher alpha ITC was associated with higher accuracy (** p < 0.01).
