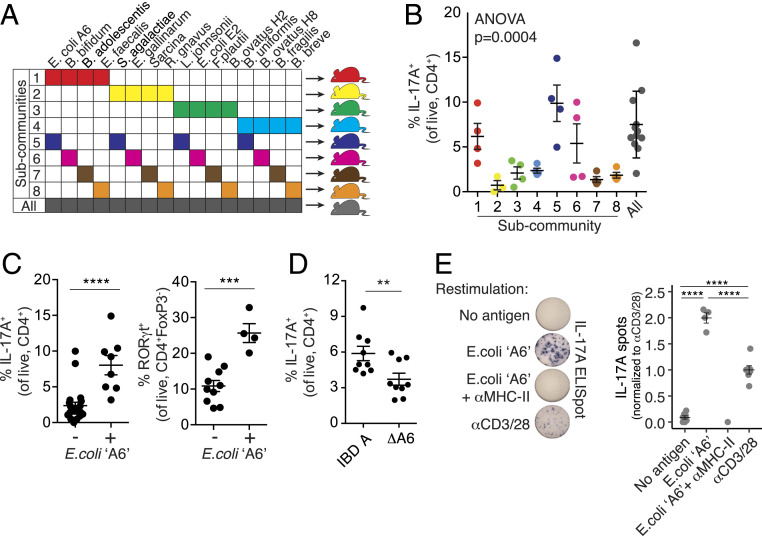
Fig. 3.
Identification of a Th17-inducing strain from a donor with Crohn’s disease. (A) Groups of germ-free B6 mice were each colonized with one of eight communities comprised of 4 of the 16 strains isolated from donor IBD A. (B) The proportion of IL-17A+ CD4+ T cells (of live CD4+ cells) in the colon lamina propria of mice colonized with each subcommunity derived from the IBD A microbiota. (C) The proportion of IL-17A+ CD4+ T cells and RORγt+ Th17 cells in mice colonized with communities in which E. coli strain A6 was present (+) or absent (−). (D) The proportion of IL-17A+ CD4+ T cells (of live CD4+ cells) in the colon lamina propria of mice colonized with the complete IBD A microbiota or a modified version of IBD A lacking E. coli strain A6 (ΔA6). (E) IL-17A secretion from mLN CD4+ T cells isolated from mice colonized with IBD A and restimulated ex vivo with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 or dendritic cells loaded with E. coli strain A6, with or without an MHC-II blocking antibody. Plots show the mean and SE of each group of mice, and P values were calculated by t test (C and D), ANOVA (B), and ANOVA with Tukey correction (E). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.