Figure 5.
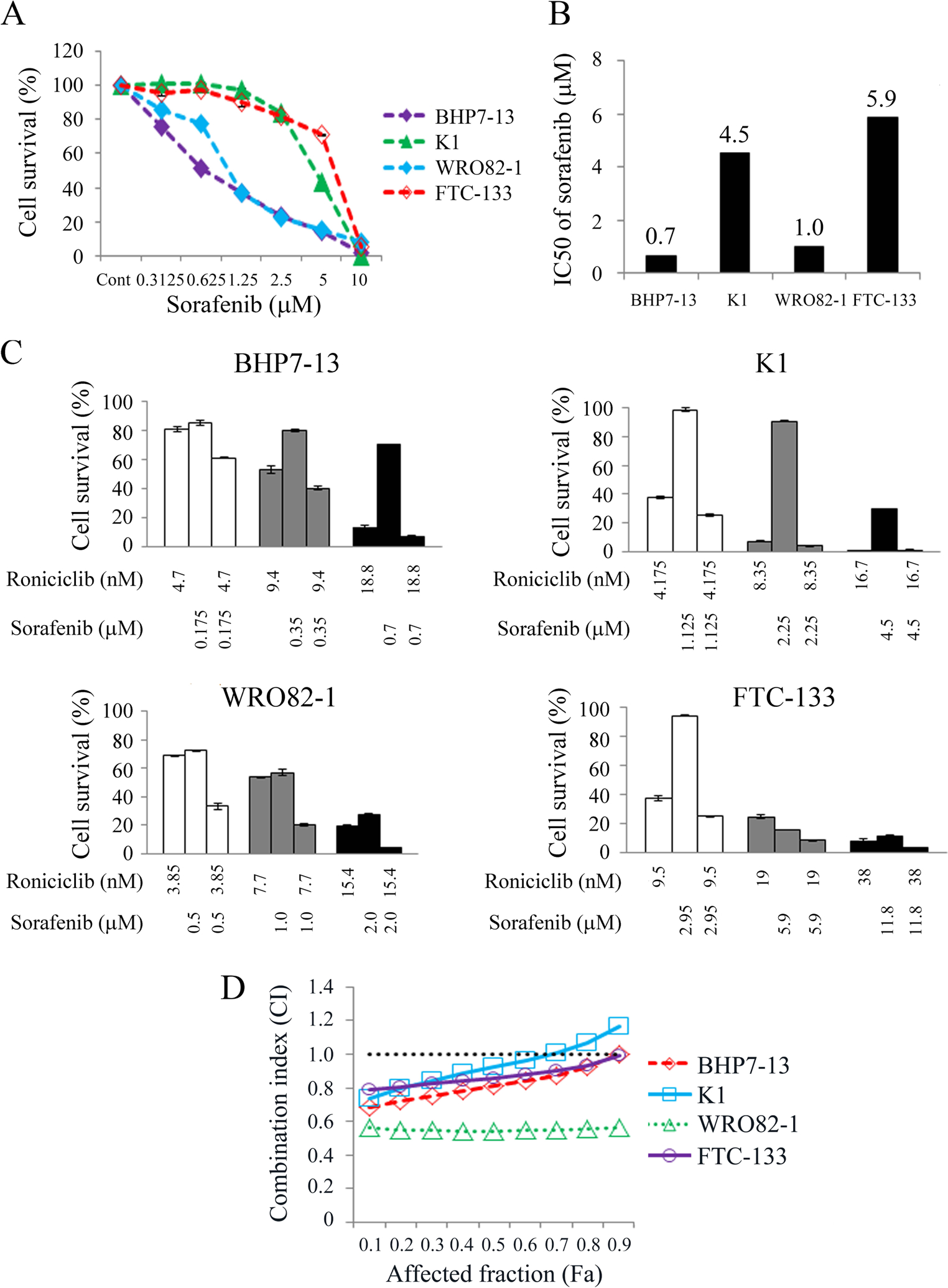
Combination therapy of roniciclib and sorafenib in well-differentiated thyroid cancer cells. (A) Cytotoxicity was evaluated in BHP7–13, K1, WRO82–1 and FTC-133 cells treated with a series of six two-fold dilutions of sorafenib starting at 10 μmol/L. Dose-response curves were obtained on day 4 using LDH assays. (B) The median-effect dose (IC50) of sorafenib on day 4 was calculated for each cell line using CompuSyn software. (C) The cytotoxic effects of roniciclib and sorafenib alone and in combination after a 4-day treatment in BHP7–13, K1, WRO82–1 and FTC-133 cells were evaluated using LDH assays. (D) The combination index (CI) of roniciclib and sorafenib was calculated using CompuSyn software. The combination therapy of roniciclib and sorafenib had synergistic effects in WRO82–1 and FTC-133 cells, synergistic to additive effects in BHP7–13 cells and synergistic to antagonistic effects in K1 cells. Synergistic effects appeared when the affected fractions of BHP7–13 and K1 cells was lower (affected fraction < 0.9 and < 0.7, respectively). The horizontal line at CI = 1 was drawn for discrimination of synergism (CI < 1) and antagonism (CI > 1).
