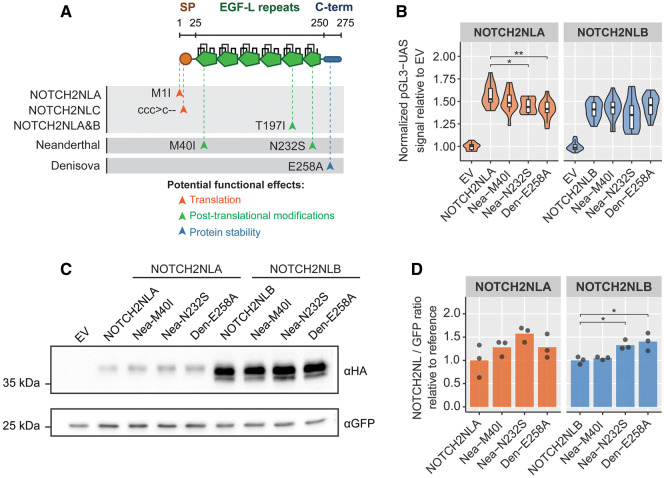
Fig. 2.
Characterization of archaic NOTCH2NL coding variants. (A) Overview of modern human, Neanderthal-specific, and Denisovan-specific coding variants. (B) Coculture NOTCH2 reporter assay testing Neanderthal and Denisovan variants reconstructed in the human NOTCH2NLA cDNA (n = 15 in three experiments, analysis of variance (ANOVA) P = 0.002, followed by Tukey’s test), or the human NOTCH2NLB cDNA (n = 20 in four experiments, ANOVA P = 0.07). (C) Western blot analysis of Neanderthal and Denisovan variants. Plasmids were transfected in equimolar amounts. (D) Quantification of protein level from three independent experiments for NOTCH2NLA (ANOVA P = 0.12) and NOTCH2NLB (ANOVA P = 0.006, followed by Tukey’s test). Asterisks indicate significant values from Tukey’s post hoc tests: *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.