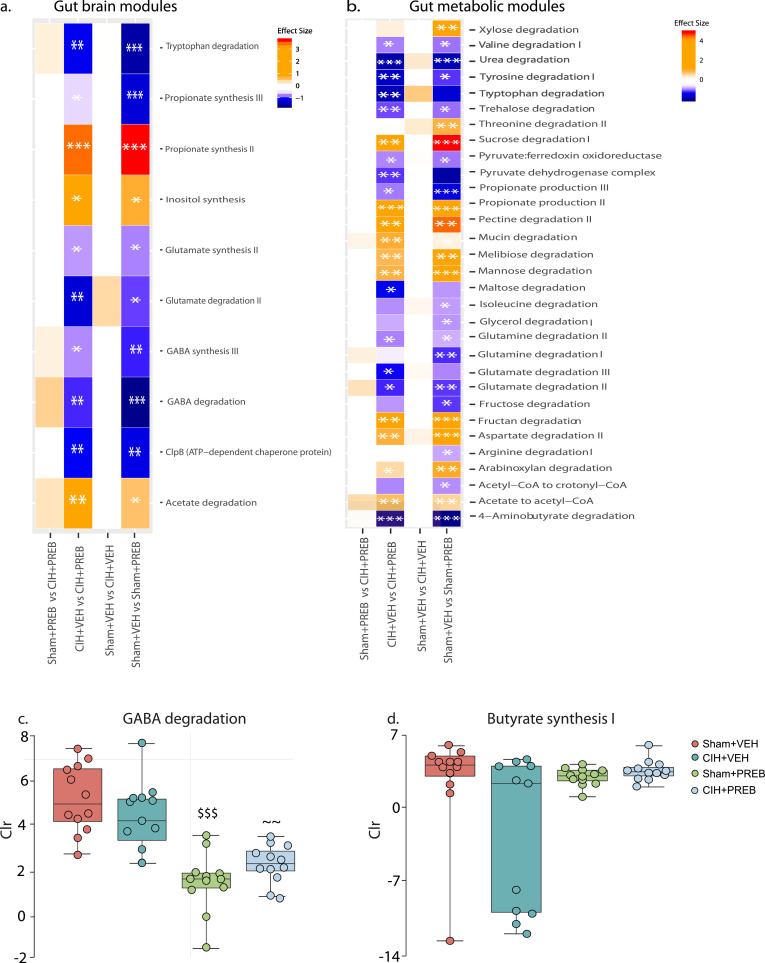
Fig. 8.
Prebiotic administration alters GBMs and GMMs
Group data for GBMs (a) and GMMs (b) in heatmap representation, GABA degradation (c) and Butyrate synthesis I (d) in Sham+VEH, CIH+VEH, Sham+PREB and CIH+PREB. CIH, chronic intermittent hypoxia; PREB; prebiotic; VEH, vehicle. Data (c-d) are expressed as box and whisker plots (median, IQR and minimum to maximum values); n = 11–12. A pairwise implementation of the aldex.ttest() function was used to compare multiple groups. CIH exposure did not alter GBMs and GMMs. Prebiotic administration significantly modulated many metagenomes of the GBMs and GMMs. A positive effect size indicates an increase in prebiotic treated rats, a negative effect size indicates a decrease in prebiotic treated rats. Benjamini-Hochberg corrected q-values,* q<0.05, ** q<0.01, *** q<0.001. GABA degradation and Butyrate synthesis I diverge in CIH-exposed compared with Sham rats, depending on prebiotic administration. ~ p<0.01, CIH+PREB versus CIH+VEH; $$$ p< 0.001, Sham+PREB versus Sham+VEH.