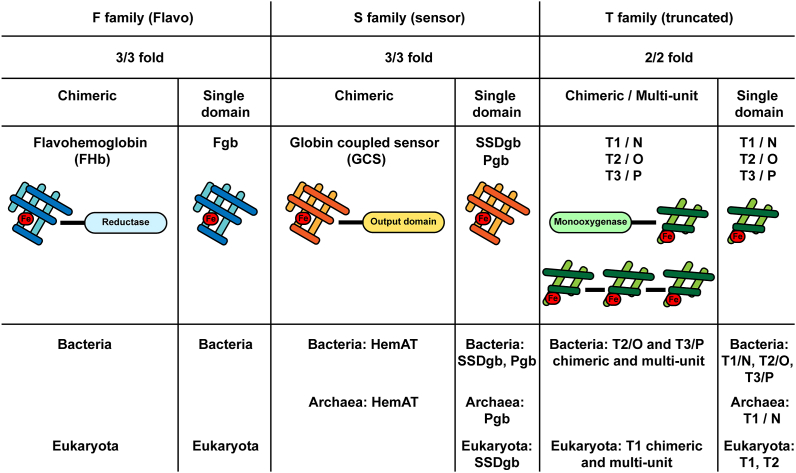
Fig. 1.
The three globin families. The F (Flavo) family, the S (Sensor) family and the T (Truncated) family can all be found in a chimeric or in a single domain configuration. T globins may further display multi-unit assemblies. Chimeric (FHb) and single-domain (Fgb) F globins are found in bacteria and eukaryotes, but absent in archaea, and are numerically preponderant. S family globins include chimeric globin-coupled sensor proteins (GCS) which carry a C-terminal output domain (including HemAT for aerotactic heme sensor), and sensor single domain globins (SSDgb) and their shorter version the protoglobins (Pgb). HemAT is found in bacteria and archaea, SSDgbs are found in bacteria and eukaryotes, and Pgb in bacteria and archaea. T family globins exist in three structural subfamilies, T1, T2 and T3, which, in bacteria, are also termed N, O and P, respectively. Chimeric and multi-unit T globins can be found in bacteria (T2/O and T3/P) and eukaryotes (T1), whereas single domain T globins appear in bacteria (T1/N, T2/O and T3/P), in archaea (T1/N) and eukaryotes (T1 and T2).