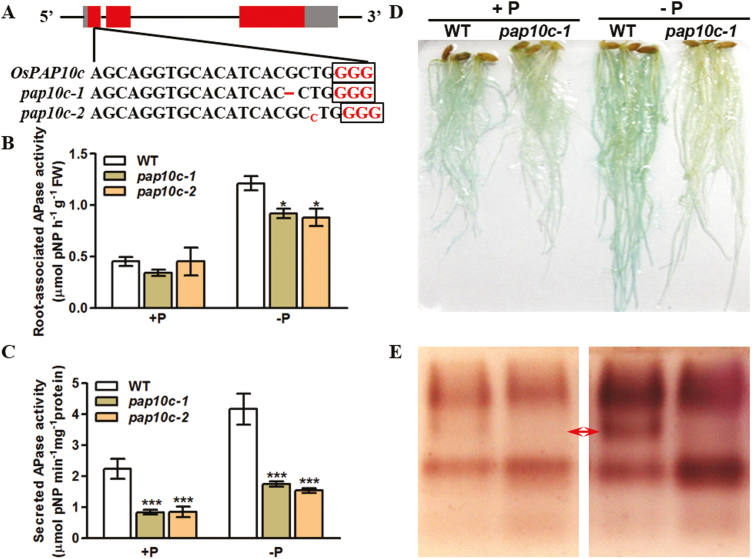
Fig. 2.
APase activity in rice Ospap10c mutants. (A) Schematic diagram of deletion mutations at the target sites in two representative knock-out lines generated by CRISPR/Cas9 technology. The sgRNA target sequence is shown and the protospacer adjacent motifs are indicated by the boxes. (B) Root surface-associated APase activity of the wild-type (WT) and pap10c mutants under +P and –P conditions. (C) Secreted APase activity of the WT and pap10c mutants under +P and –P conditions. (D) BCIP staining of the WT and the pap10c-1 mutant under +P and –P conditions. (E) In-gel APase activity assay of secreted proteins extracted from suspension cells of the WT and pap10c-1 mutant. The arrows indicate that the absence of a specific APase isoform in the mutant under Pi-deficient conditions.