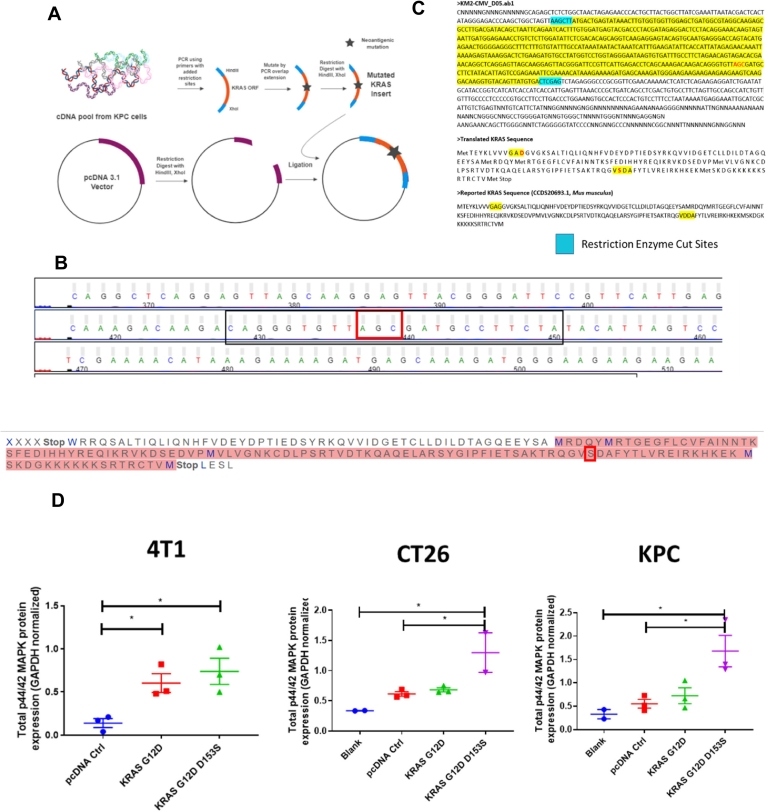
Fig. 2.
Designing plasmids encoding mutant KRAS and determining functionality of mutant KRAS, a) Workflow for designing plasmids encoding KRAS with mutations predicted to generate neoantigens, mutations were incorporated into DNA inserts via PCR overlap extension, b) Sanger sequencing results confirm incorporation of the D153S mutation- the mutation predicted to have highest binding to MHC-I alleles for C57BL/6 mice, sharing genetic background with KPC, c) Sanger sequencing results confirm incorporation of the D153S mutation in plasmids with pcDNA3.1 backbone, d) Western blot analysis of lysates from in vitro cell cultures transfected with KRAS ORF plasmids for 48 h, using Lipofectamine 2000 transfection reagent, analyzing for p44/42 MAPK, downstream of RAS (n = 2–3). Data show mean ± SEM. * p < .05.