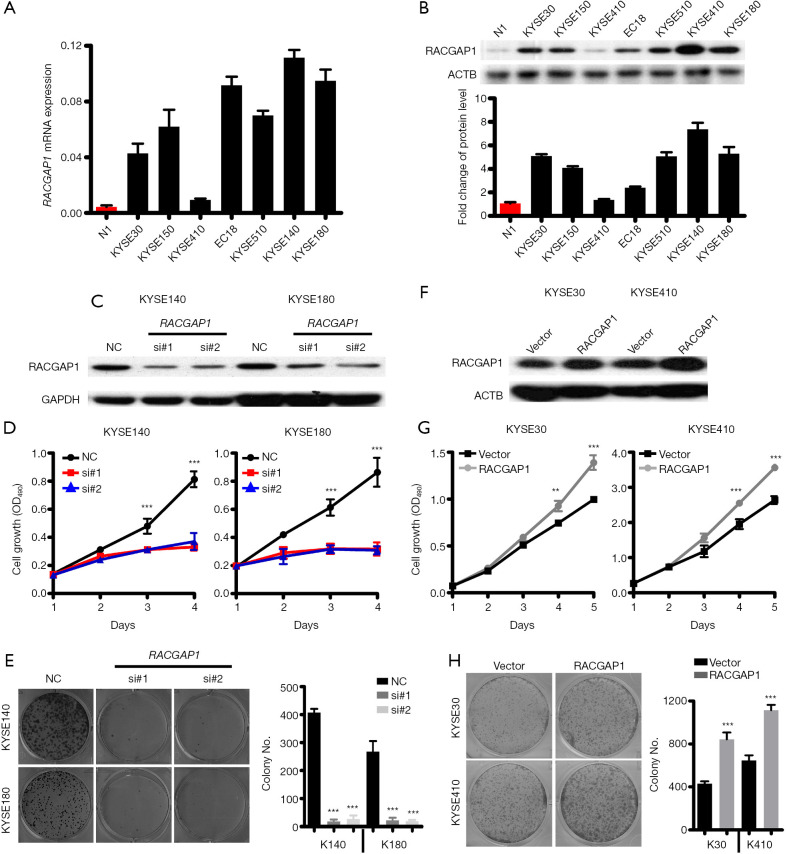
Figure 2.
RACGAP1 as an oncogenic driver in ESCC. (A,B) QPCR assay (A) and Western blotting assay (B) shown that the RACGAP1 mRNA level is highly upregulated in 6/7 ESCC cell lines compared with healthy esophageal epithelial cells. (C) Western blotting assay shown RACGAP1 was knockdown in KYSE140 and KYSE180 by two specific siRNAs. (D) MTT assay showed that RACGAP1 depletion strongly inhibits the cell growth of KYSE140 and KYSE180. (E) Colony formation assay showed that RACGAP1 depletion suppressed the proliferation of KYSE140 and KYSE180. (F) The western blotting assay showed stable overexpression of RACGAP1 in KYSE30 and KYSE410 cell lines. (G) MTT assay showed that RACGAP1 overexpression enhances the cell growth of KYSE30 and KYSE410. (H) Colony formation assay showed that RACGAP1 overexpression promoted the proliferation of KYSE30 and KYSE410. The data are presented as means ± SEMs. The P values were determined with Student’s t-test (two groups) or one-way ANOVA (three groups). **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. ESCC, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.