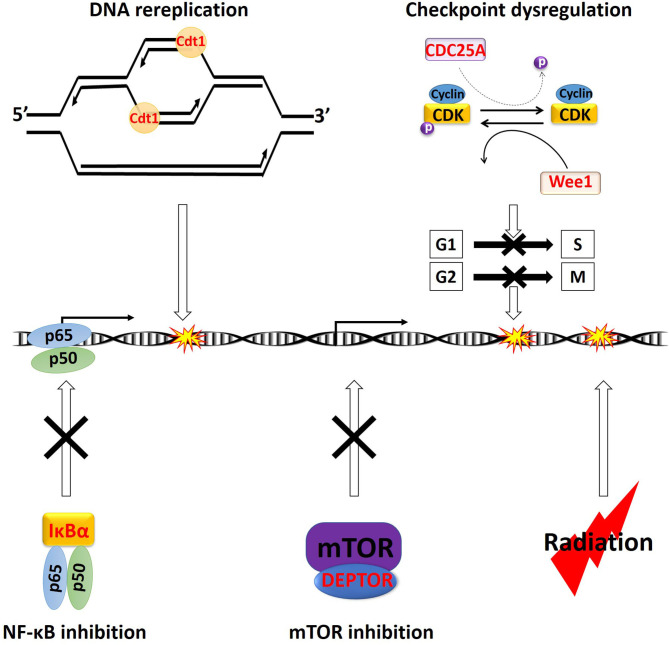
Figure 2.
Overview of the major cytotoxic mechanism of NEDDylation inhibition. All the characters in “Red” color are CRL substrates. Accumulation of Cdt1 can trigger DNA rereplication, resulting in DNA damages. Stabilization of CDC25A can potentially cause dysregulation of both early (G1 phase to S phase) and late (G2 phase to M phase) cell cycle checkpoints (dash arrow). Meanwhile, the accumulation of Wee1, p21, and p27 will trigger cell cycle arrest at the G1 or G2 phase. Stabilization of IκBα will lead to sequestration NF-κB p65 and p50 heterodimer in the cytosol, leading to inhibition of its transcriptional activities. Stabilization of DEPTOR can directly inhibit mTOR. Ionizing radiation also triggers cell death via induction of DNA damages. p, phosphor group.