Figure 4.
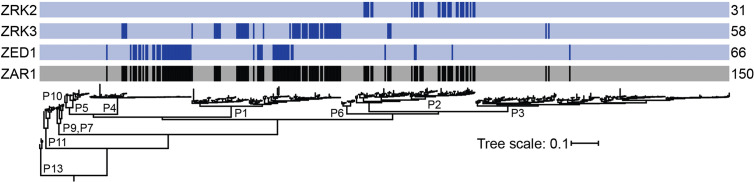
ZAR1 uses a diversity of kinase sensors to recognize P. syringae. Specific ZAR1/ZRK modules confer putative resistance to predominantly independent P. syringae clades. The generation of this P. syringae core genome phylogeny, with associated phylogroup designations (P) is described in Laflamme et al., 2020. Colored bars above the phylogeny represent strains that harbor an ETI eliciting allele that requires ZAR1 (black) and the specific ZRK required for each ZAR1 ETI (blue): ZED1, ZRK3 and ZRK2. Numbers indicate the total number of strains that carry a T3SE whose ETI requires the associated genetic component. Putatively truncated sequences (less than 75% the length of the representative allele) are not displayed (Laflamme et al., 2020).