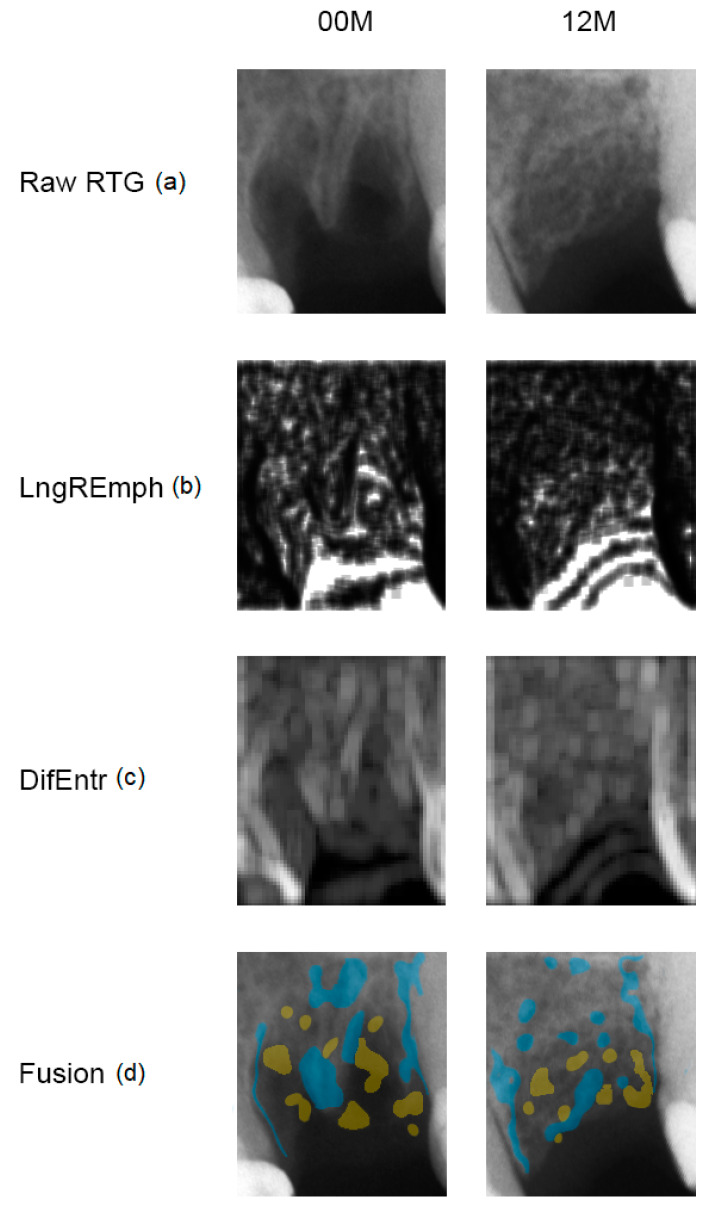
Figure 1.
Collagen-guided alveolar crest augmentation. Raw RTG (a): intraoral radiograph immediately after collagen implantation into the alveolar (00 M) and at a 12-month follow-up (12 M). LngREmph (b): a map of the occurrence of long chains of pixels of similar optical density; brighter fields indicate more of such occurrences in the X-ray image. DifEntr (c): map of regions with chaotically arranged small elements recorded in the X-ray; brighter places indicate a more chaotic microstructure. Fusion (d): the application of places on the raw X-ray which represent the largest occurrence of long pixel chains (yellow = high LngREmph) in the alveolar crest and the most chaotic places (blue = high DifEntr). Please note that yellow areas do not coincide with blue areas. This is due to the detection of the different structurally different alveolar regions, i.e., LngREmph = radiolucent regions = soft tissue, while DifEntr = trabecular regions = bone.