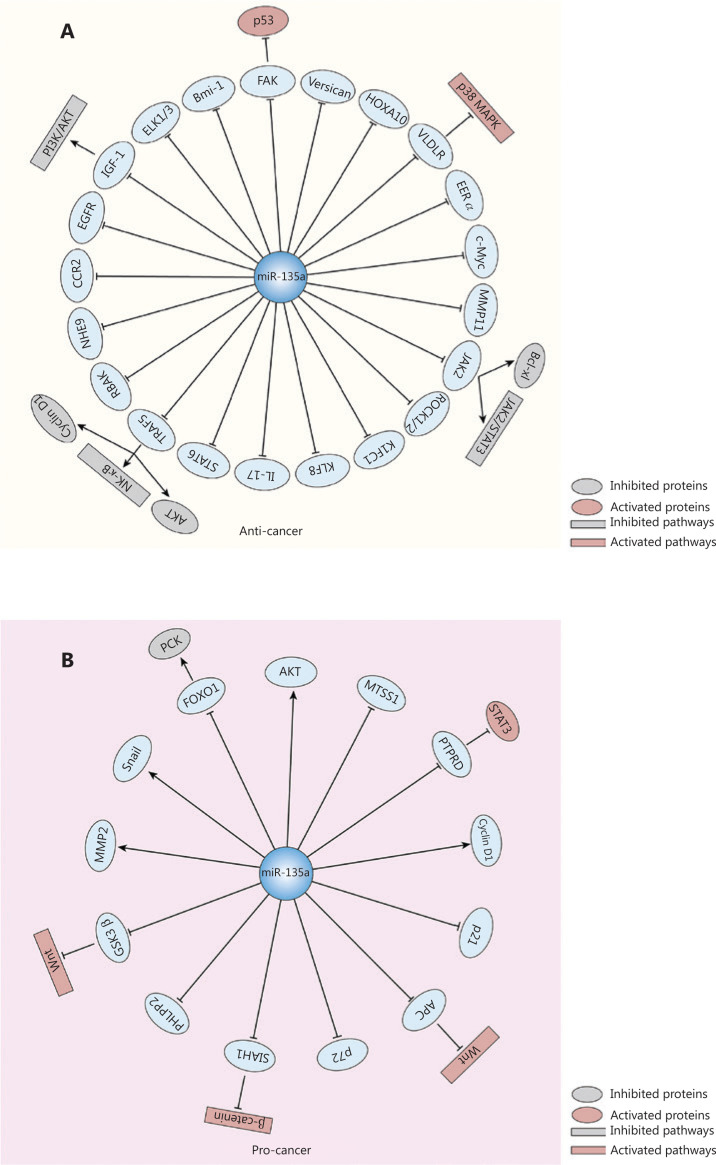
Figure 3.
The effects of miR-135a on cancer progression and relevant targets and signaling pathways. (A) The miR-135a could inhibit the progression of cancer by targeting various mRNAs, which led to the inactivation of several pathways, including the PI3K/AKT pathway, JAK2/STAT3 pathway, and NF-κB pathway, as well as the activation of the p38 MAPK pathway and the p53 cancer suppressor gene. (B) The miR-135a can also promote cancer development via the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and STAT3, and the inactivation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase.