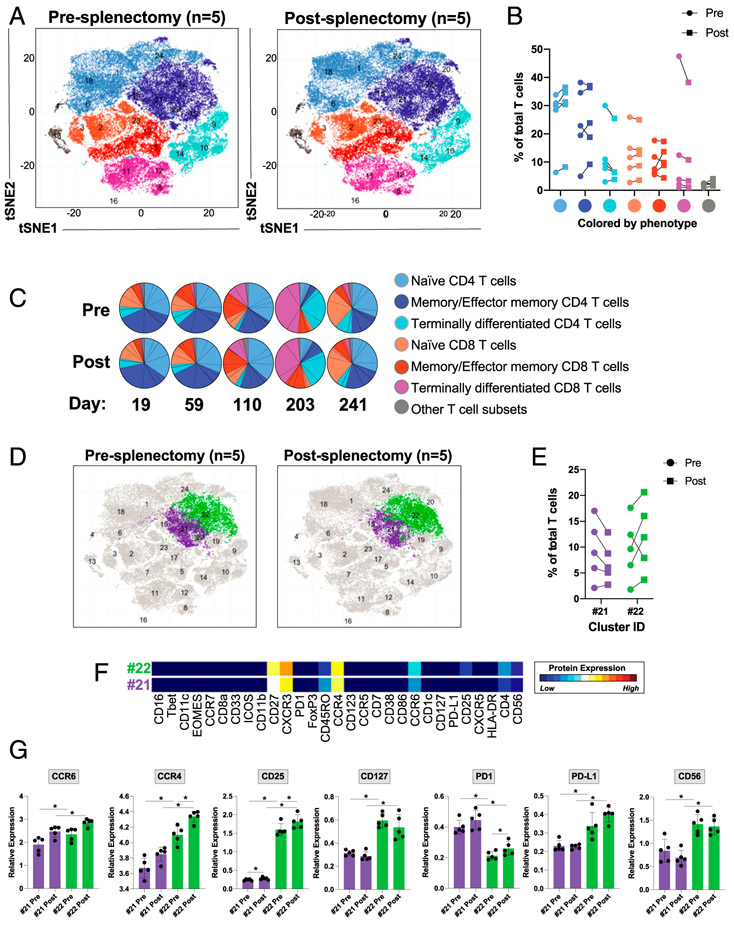
FIGURE 4. Splenectomy increases the frequency of naive CD4+ T cells, activates memory or effector memory CD4+ T cells, and increases the expression of CCR6 and CCR4 on these cells.
Mass cytometric analysis of lysed whole blood from patients before and after splenectomy. (C) The timing of the postsplenectomy blood draws from each patient. Files were normalized and gated on single CD45+CD3+CD19− cells prior to analysis. (A) PhenoGraph analysis of CD45+CD3+CD19− cells comparing pre- and postsplenectomy samples from all five patients, colored by cellular phenotype. (B) The frequencies of PhenoGraph-defined clusters comparing the values of each cell type between pre- and postsplenectomy samples from each patient (cell populations were identified based on the markers in Supplemental Table III). (C) Comparison of the frequencies of PhenoGraph-defined clusters between pre- and postsplenectomy samples from each patient, including the number of days postsplenectomy the blood draw occurred. (D and E) Identification of the two populations with the greatest degree of change between pre- and postsplenectomy. (F) Dendrogram heatmap generated in Cytofkit depicting the differences in the expression of the designated proteins between clusters 21 and 22. (G) Quantification of the mean metal intensity (relative expression level) of the designated proteins compared between clusters 21 and 22 from pre- and postsplenectomy samples. *p < 0.05.