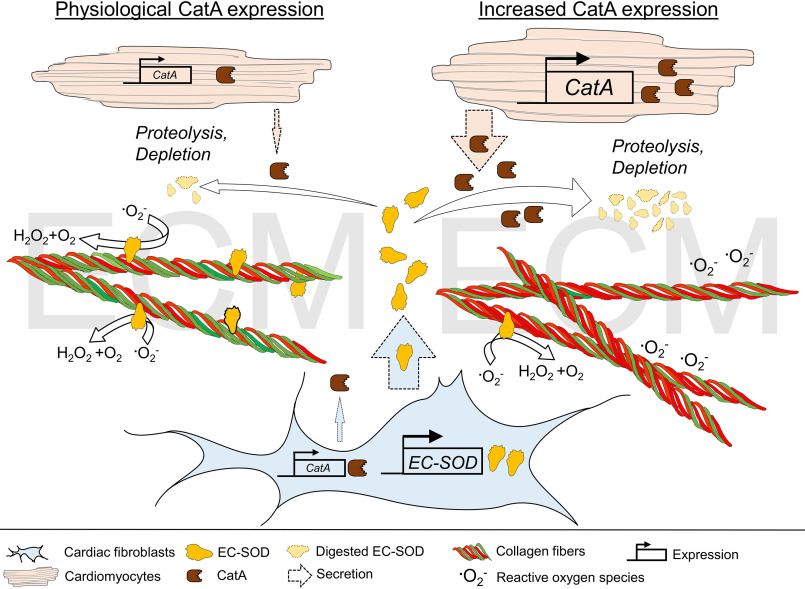
Figure 7.
Summary. The antioxidant enzyme EC-SOD is expressed and secreted in abundance into the ECM by CFs. In the ECM, EC-SOD protects against reactive oxygen species by dismutation of .O2− to H2O2 and O2. The carboxypeptidase CatA is expressed by both CFs and CMs and secreted into the extracellular space, where it proteolytically degrades EC-SOD, thereby regulating EC-SOD distribution in the ECM. Cardiomyocyte-specific overexpression of CatA leads to enhanced EC-SOD protein degradation and accelerated depletion from the ECM, subsequently increasing vulnerability to reactive oxygen species, followed by cardiac fibrosis formation with a higher quantity of collagen type I fibers (red fibers) and myocardial hypertrophy.