Figure 5.
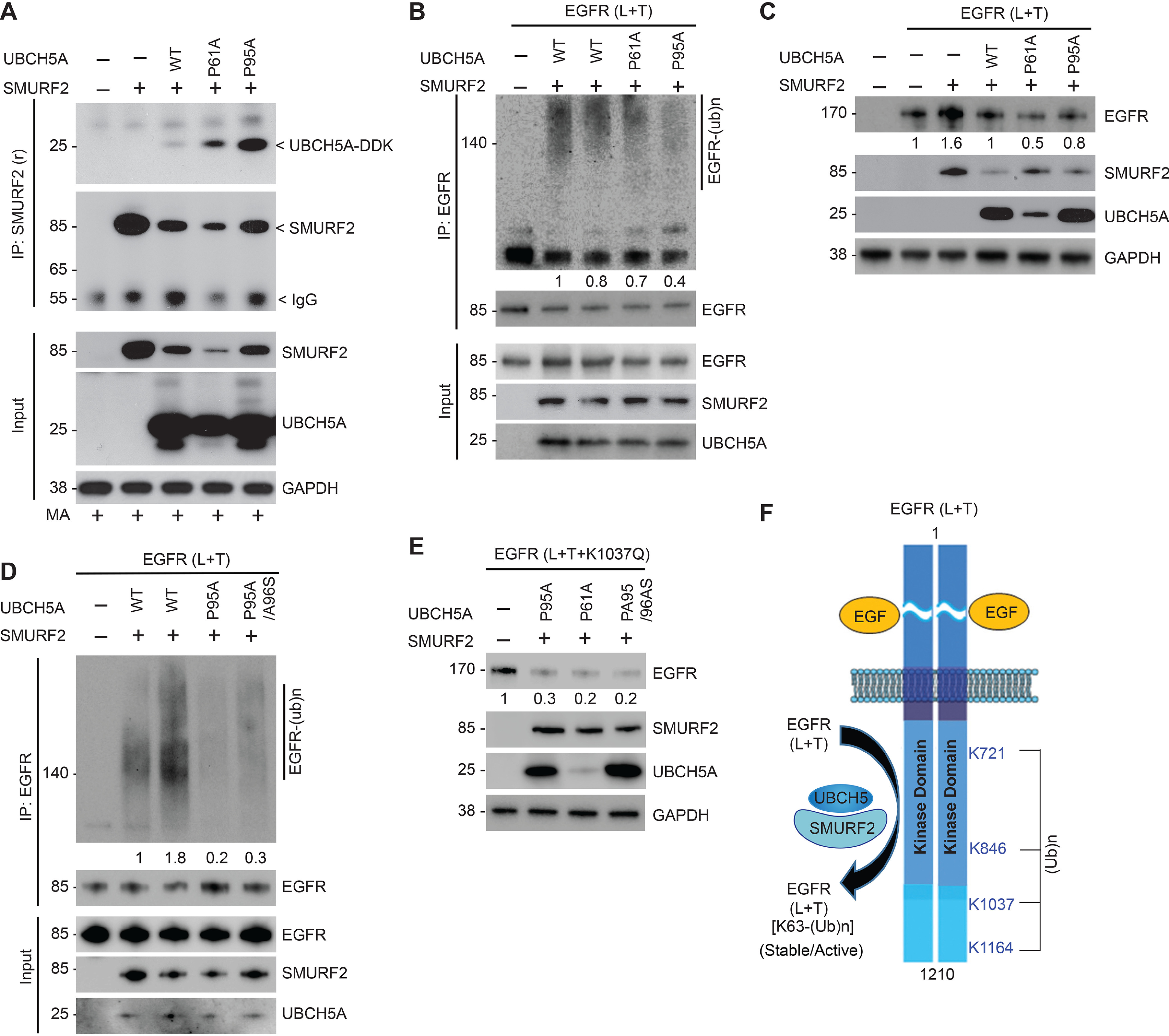
Alteration of SMURF2-UBCH5 protein–protein interaction impacts mutant EGFR levels. A, Flag-tagged SMURF2 and Myc-tagged UBCH5A (WT, P61A, and P95A mutants) were overexpressed in HEK293 cells. Cell lysates were prepared 24 h posttransfection and subjected to immunoprecipitation using SMURF2 antibody followed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. B, to determine catalytic activity of P61A and P95A mutant UBCH5A, E2 proteins were synthesized using a TNT T7 quick-coupled in vitro transcription/translation system, followed by in vitro ubiquitination assay using recombinant EGFR (L+T) and SMURF2 proteins. Reactions were then subjected to immunoprecipitation using EGFR antibody followed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. The total amount and catalytic activity of commercially available UBCH5A (lane 2) were comparable with WT UBCH5A protein synthesized using an in vitro transcription/translation system (lane 3). C, effect of overexpression of UBCH5A (WT and P61A and P95A mutants) along with SMURF2 on L858R/T790M EGFR steady-state levels. D, comparison of in vitro ligase activity of mutant UBCH5A (P95A and P95A/A96S) compared with WT E2 obtained either commercially (lane 2) or synthesized using the TNT system (lane 3) as described above. E, HEK293 cells overexpressing EGFR (L+T+K1037Q) mutant were transfected alone or in combination with the indicated UBCH5A mutants (P95A, P61A, or P95A/A96S), and cell lysates prepared 48 h posttransfection followed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. F, schematic diagram showing lysine (K) residues (K721, K846, K1037, and K1164) as identified residues that underwent SMURF2-mediated ubiquitination as determined using MS analyses. We propose altering the SMURF2-UBCH5 interaction as a future targeting strategy to promote protein destabilization of mutant EGFR to overcome TKI resistance.
