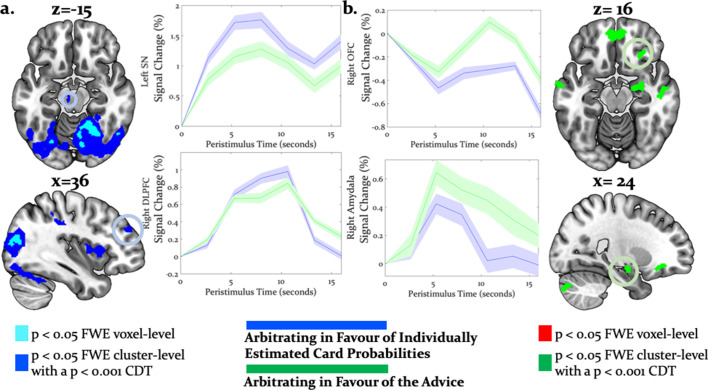
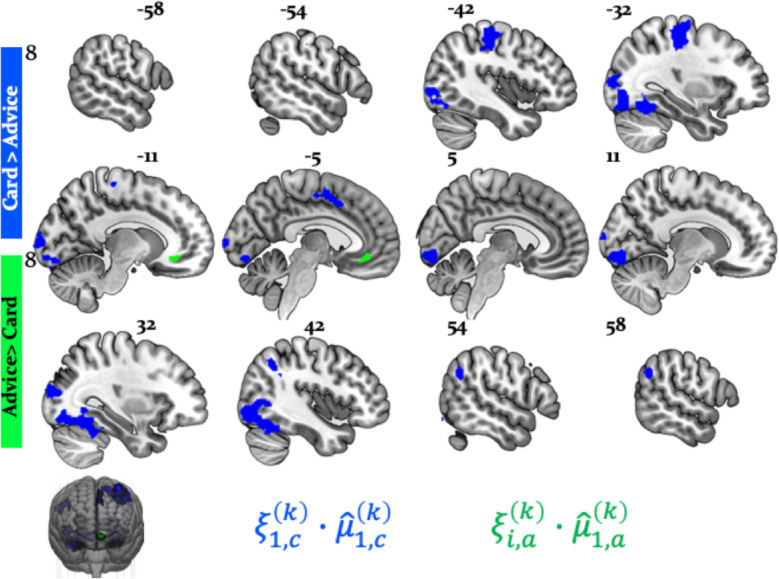
Figure 7. Neural arbitration directed to specific source of information.
(a) Activity in the left midbrain (substantia nigra (SN)) [−6,–18, −10] (top) and the right DLPFC [36, 46, 30] (bottom) during the prediction of card color increased more when participants arbitrated in favor of individually estimated card color probability as compared to the advisor’s suggestions (whole-brain FWE cluster-level corrected, p<0.05). (b) Activity in right (OFC [28, 26, -16] (top) and in right amygdala [18, -10, -16] (bottom) increased more when participants arbitrated in favor of the advisor’s suggestion than when they arbitrated in favor of the individually learned estimates of card probability (whole-brain FWE cluster-level corrected, p<0.05). The line plots reflect the average BOLD signal activity in the respective significantly activated cluster aligned to the onset of advice presentation relative to pre-advice baseline averaged across trials for one representative participant in midbrain and DLPFC (a) or OFC and amygdala (b). The shaded areas depict + / - standard error of this mean. In this figure, the scales reflect t-values.