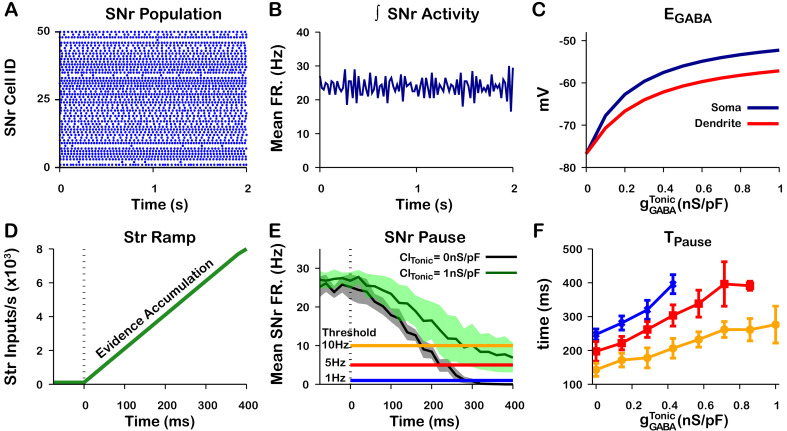
Figure 13. Tonic somatic conductance affects somatic and dendritic and tunes SNr responses to Str inputs.
(A) Raster plot of spikes in the simulation of an SNr network model containing 50 simulated neurons that receive tonic somatic inhibition from GPe projections. (B) Integrated SNr population activity gives a mean firing rate of about 23 Hz, as seen in in vivo conditions (Freeze et al., 2013; Mastro et al., 2017; Willard et al., 2019). (C) Increasing tonic depolarizes somatic and dendritic . (D) Ramping Str synaptic inputs used to represent evidence accumulation in a perceptual decision-making task. (E) Inhibition and pause generation in the SNr during evidence accumulation/ramping Str activity, for two different tonic somatic conductances. (F) Increasing the tonic conductance lengthens , the time for the SNr firing rate to drop below threshold (colors correspond to threshold levels in E). If the tonic conductance becomes too great, then SNr firing cannot be pushed to arbitrarily low rates. .