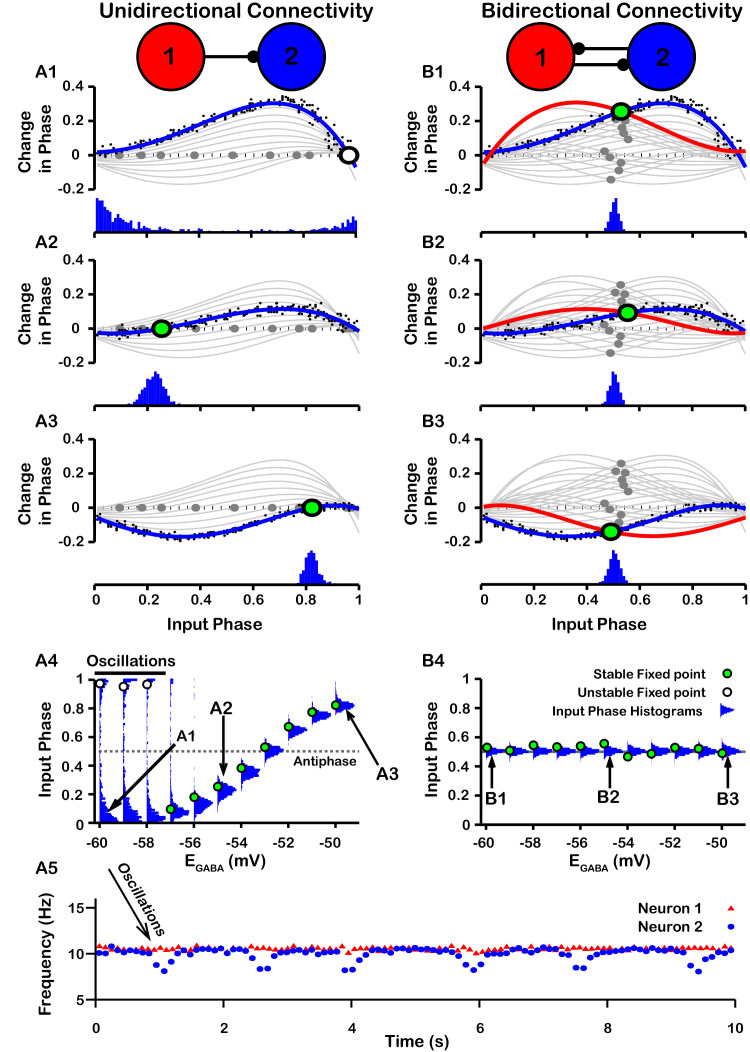
Figure 8. Effect of on SNr synchrony in a unidirectional (left) and bidirectional (right) synaptically connected two-neuron network.
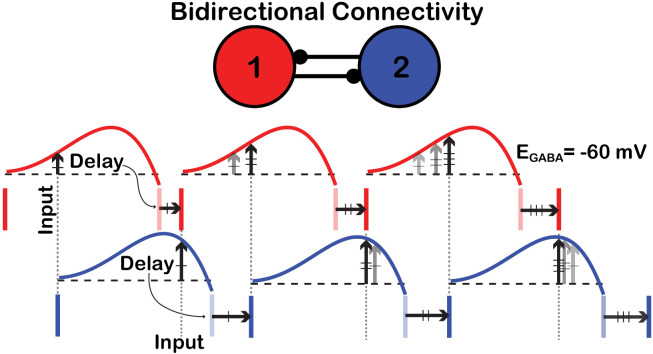
(A1-A3 and B1-B3) (Top) Identification of PRC fixed points and (Bottom) histogram of the timing of synaptic inputs in the phase of neuron 2 (Input Phase) as a function of . Recall that positive changes in phase correspond to delays. (A1,B1) ; (A2,B2) ; (A3,B3) . Black dots indicate dataset used to generate PRC in red/blue. Stable and unstable fixed points are indicated by green and white filled circles, respectively. For reference, all PRCs and fixed points are included in gray for all values of tested. (A4,B4) Effect of on SNr phase locking. Blue histograms show the distribution of synaptic inputs relative to the phase of neuron 2 (input phase) for the two network simulations for different levels of . Green and white filled circles indicate the stable and unstable locking predicted by analysis of PRCs. Note the unstable fixed points for the lowest values of in the unidirectional case. (A5) In the unidirectional case, slow 1 Hz oscillations in the frequency of neuron 2 arise due to phase slipping at hyperpolarized values of .