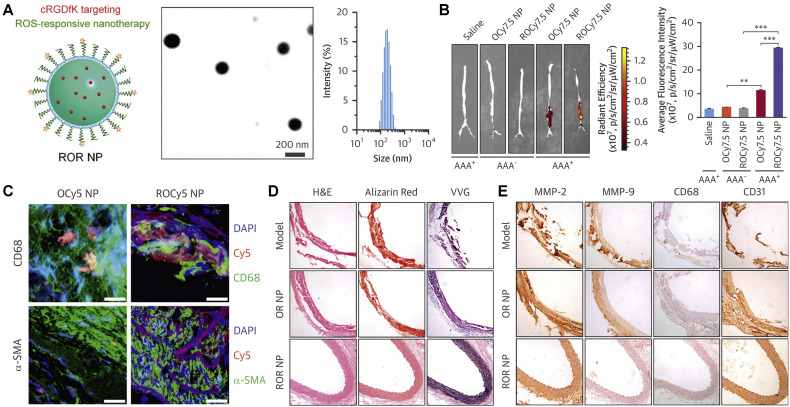
Fig. 8.
A targeting nanotherapy for abdominal aortic aneurysms. (A) Schematic (left), TEM image (middle), and size distribution (right) of ROR NP. (B) Ex vivo images (left) and histograms (right) showing accumulated ROCy7.5 NP or OCy7.5 NP in aneurysmal aortas. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (C) Immunofluorescence analysis of localized ROCy5 NP in aneurysms. Scale bars, 20 μm. (D) H&E, Alizarin Red, or VVG stained histological sections of aneurysmal aortas. (E) Immunohistochemistry analyses of aneurysmal aortas. OR NP, RAP-containing OxbCD nanotherapy; ROR NP, a ROS-responsive, cRGDfK targeting RAP nanotherapy; OCy5 NP, Cy5-labeled OxbCD nanoparticles; ROCy5 NP, Cy5-labeled OxbCD nanoparticles with cRGDfK decoration; OCy7.5 NP, Cy7.5-labeled OxbCD nanoparticles; ROCy7.5 NP, Cy7.5-labeled OxbCD nanoparticles decorated with cRGDfK. Reproduced with permission [329]. Copyright 2018, Elsevier.