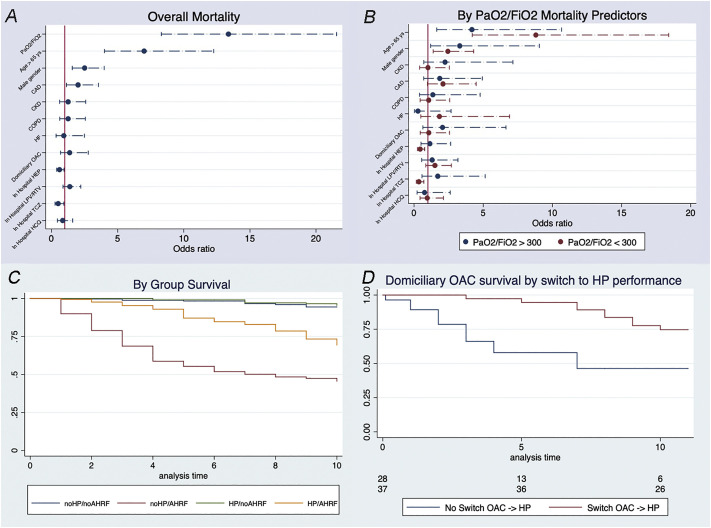
Fig. 1.
panel A-B-C-D.
Panel A-B: multivariable logistic-regression analysis showing independent overall (panel A) and by group (panel B) predictors of in-hospital death.
Panel C: Kaplan–Meier curves depicting mortality rates for OAC patients who were or were not switched to heparin during hospitalization. Log rank p for every group: No HEP/No AHRF vs No HEP/AHRF p < 0.001; No HEP/No AHRF vs HEP/No AHRF p < 0.585; No HEP/No AHRF vs HEP/AHRF p < 0.001; No HEP/AHRF vs HEP/No AHRF p < 0.001; No HEP/AHRF vs HEP/AHRF p < 0.001; HEP/No AHRF vs HEP/AHRF p < 0.001.
By group hazard ratios: No HEP/No AHRF 0.215 (CI 0.125–0.371); HEP/No AHRF 0.196 (CI 0.117–0.330); No HEP/AHRF 6.439 (CI 4.668–8.882); HEP/AHRF 0.869 (CI 1.367–2.557). All p < 0.01.
Panel D: Kaplan–Meier curves depicting mortality rates for patients who were or were not treated with heparin during hospitalization in the presence or absence of AHRF. Hazard ratio for switching from OACs to HEP: 0.213 (CI 0.079–0.575, p < 0.001).
Abbreviations
AHRF: acute hypoxemic respiratory failure
CAD: coronary artery disease
CI: confidence interval
CKD: chronic kidney disease
COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
HCQ: hydroxychloroquine
HEP: heparin
HF: heart failure
LPV/RTV: lopinavir/ritonavir
OAC: oral anticoagulant
P/F: PaO2/FiO2 ratio
TCZ: tocilizumab
ys: years.