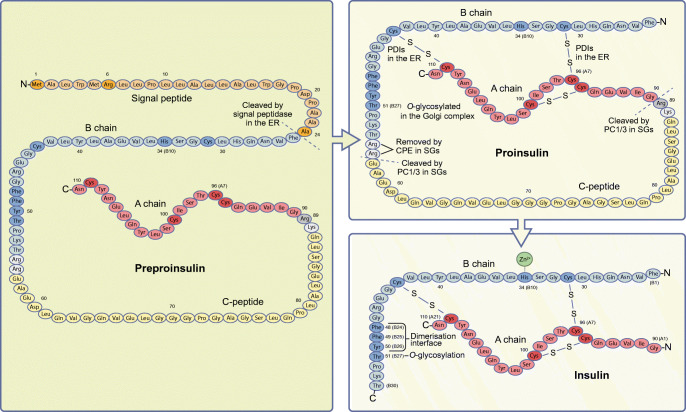
Fig. 1.
The insulin peptide. Insulin is synthesised as a 110 amino-acid-long preproinsulin including a signal peptide (orange), a B chain (blue), a connecting peptide (C-peptide, yellow) and an A chain (red). The signal peptide targets the preproinsulin to the ER, where it is cleaved by the signal peptidase and converted into proinsulin. In the ER, three disulfide bonds are formed between cysteine residues with the help of PDIs. Proinsulin is trafficked from the ER, through the Golgi and the trans-Golgi network to secretory granules (SGs), where PC1/3 and CPE process the dibasic residues (grey) to form mature insulin. Zn2+ non-covalently binds to the HisB10 to form the insulin hexamer. Amino acids mentioned in the text are shown in a darker colour. This figure is available as part of a downloadable slideset