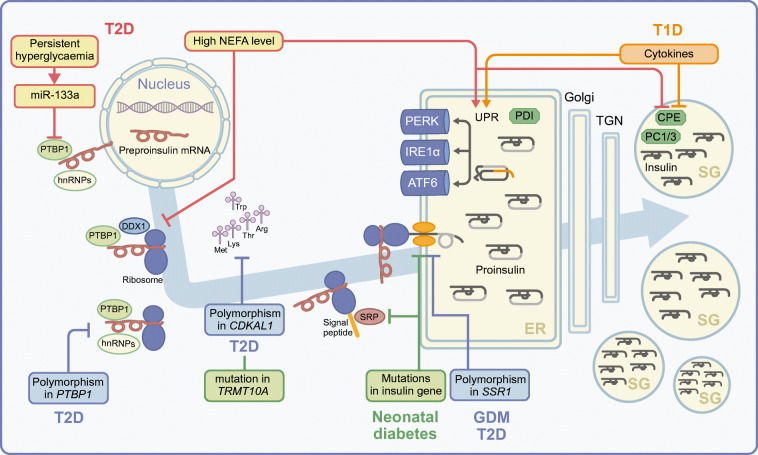
Fig. 2.
Schematic of insulin production and secretion, from mRNA to the mature hormone. The preproinsulin mRNA is stabilised by its binding to various hnRNPs in the cytosol. Preproinsulin translation and its translocation to the ER starts after the formation and activation of the ribosomal complex. Following proinsulin folding in the ER and the removal of the C-peptide, mature insulin is formed in secretory granules (SGs). Environmental changes, such as metabolic stress or inflammation, that can hamper this highly regulated process are shown in red for type 2 diabetes (T2D) and in orange for type 1 diabetes (T1D); genetic changes resulting in different types of diabetes are labelled in blue (T2D and gestational diabetes mellitus [GDM]) and in green (neonatal diabetes). ATF6, activating transcription factor 6; miR, microRNA; SRP, signal recognition particle; TGN, trans-Golgi network. This figure is available as part of a downloadable slideset