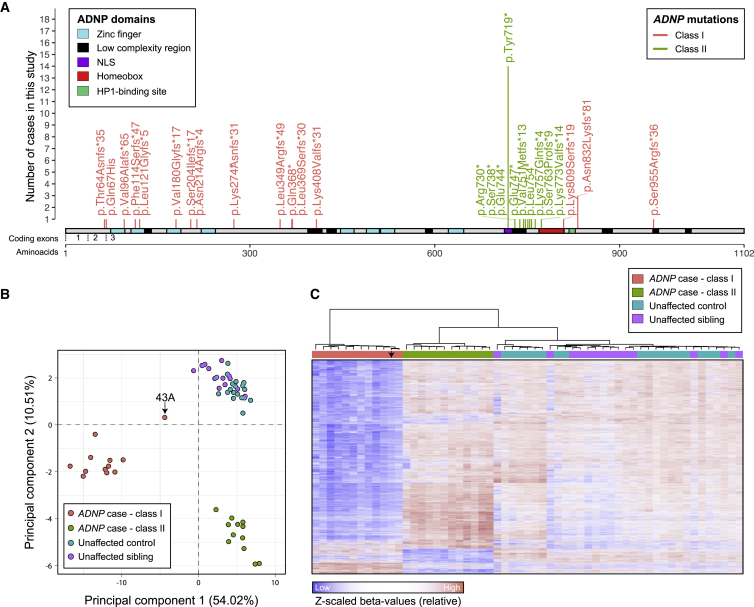
Figure 1.
Two Distinct Methylation Signatures in Individuals with HVDAS
(A) Lollipop plot of the ADNP mutations in the 42 individuals with point mutations included in the study, including the 24 with methylation data (individual 1S, who carried a deletion, is not shown, Table S1). The amino acid positions are annotated according to ADNP RefSeq protein sequence NP_056154.1. The exon annotation refers to the coding exons in NM_015339.4. The Supplemental Notes contain information on the prediction and re-annotation of linear motifs and structural domains. Mutations in the coding region from nucleotide 2156 to 2317 are classified as class II and are shown in green; mutations outside of this interval are classified as class I and are depicted in pink.
(B) Representation of the two principal dimensions in a principal component analysis of the methylation data from 12 affected individuals in class I, 12 affected individuals in class II, 19 unaffected age-matched controls, and 14 unaffected siblings. The sample indicated by an arrow (43A) harbors the most terminal class I mutation, as shown in (A).
(C) Hierarchical clustering of 12 class I affected individuals, 12 class II affected individuals, 19 unaffected age-matched controls, or 14 unaffected siblings for the 6,448 autosomal CpGs found differentially methylated in individuals with ADNP mutations belonging to class I. The arrow points to data for individual 43A, who carried the most terminal class I mutation, as shown in panel A.