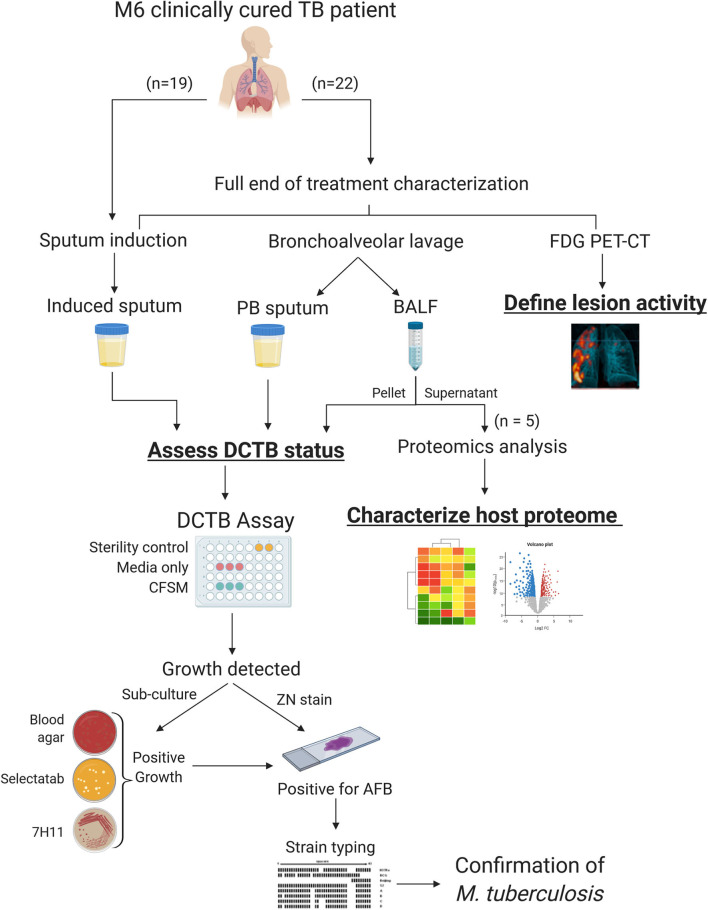
Figure 1.
Sample processing and workflow used to investigate sterilizing cure in tuberculosis (TB) patients at the end of successful anti-TB therapy. Three sample types were analyzed for DCTB M. tuberculosis in clinically cured end of treatment patients (n = 22); an induced sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and post-bronchoscopy (PB) sputum (n = 22). These patients were also scanned using FDG PET-CT to classify lesion activity at the end of treatment. The BALF supernatant from five patients was used for multiplexed proteomics analysis using tandem mass tag (TMT 10 plex) and compared to the proteome of active TB cases. A further 19 EOT patients were assessed for DCTB in their induced sputum, only. The DCTB assay consisted of a series of confirmatory tests once growth was detected including sub-culturing on blood agar, Mycobacterium Selectatab and Middlebrook 7H11 Agar. Colonies corresponding to typical growth of M. tuberculosis were subsequently picked and confirmed for acid fast bacilli (AFB) using ZN staining before being strain typed using spoligotyping.