Fig. 1.
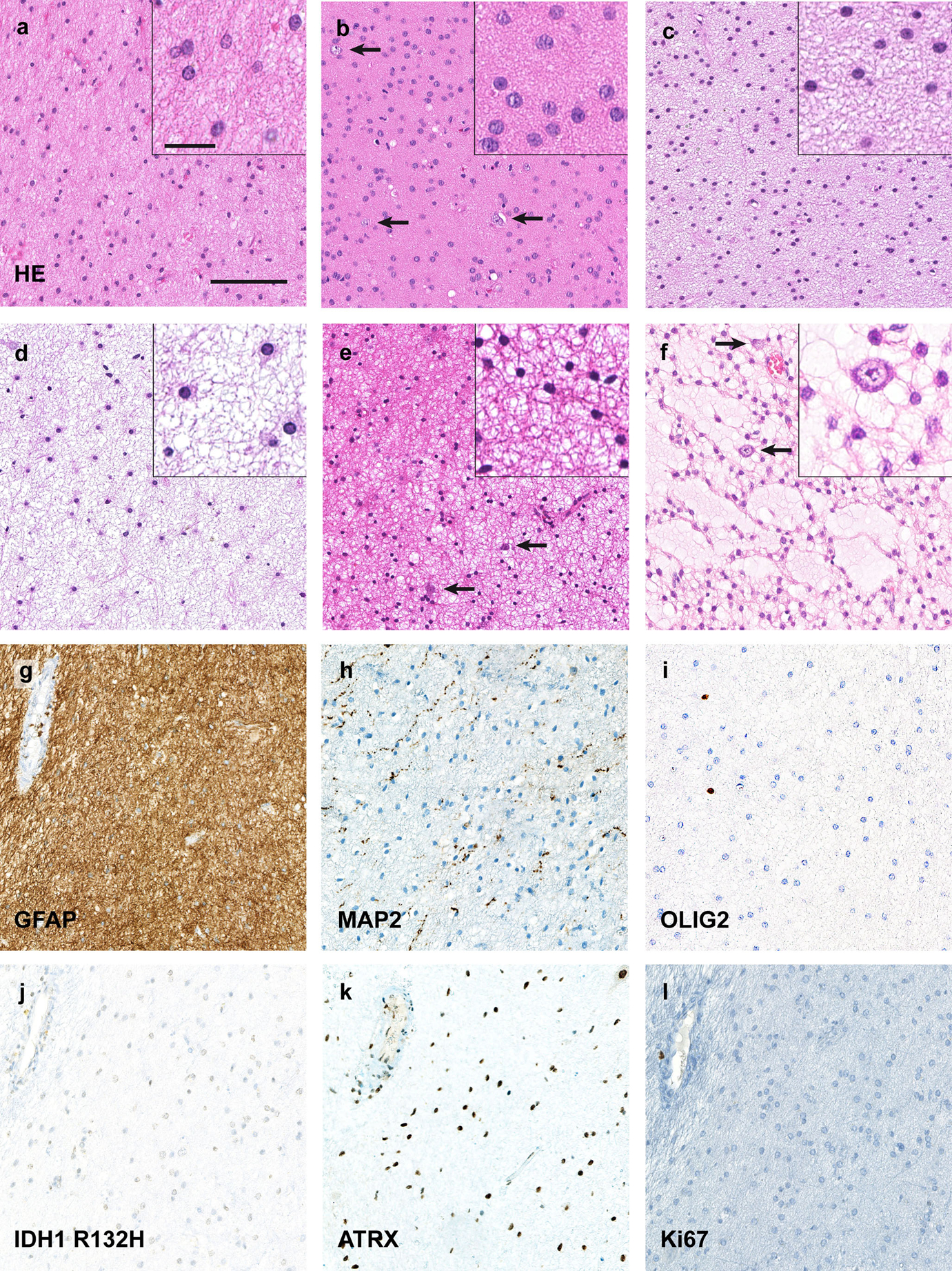
Isomorphic diffuse gliomas are monomorphic, IDH-wildtype tumours with low proliferation. a–d Histologically typical isomorphic diffuse gliomas showing round, only minimally pleomorphic nuclei, often with speckled chromatin. The cell density is slightly (a, d) to moderately (b, c) increased. The fibrillary matrix between the tumour cells can have slight (c) to extensive (d) microcystic changes. In some tumours scattered pre-existing neurons (arrows in b, e, f) are observed. e Occasionally, isomorphic diffuse gliomas may have smaller, more condensed round nuclei resembling those of oligodendrocytes. f One case focally showed myxoid changes of the matrix with scattered residual neurons, resembling the glio-neuronal element of dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumours. In other areas, the tumour also showed a clearly isomorphic growth. g–l Immunohistochemically, isomorphic diffuse gliomas are GFAP-positive (g; same tumour as in a) whereas MAP2 only labels residual neurons and neuronal processes (h). The tumours are OLIG2-negative (i) and IDH1 R132H-negative (j) with a retained nuclear expression of ATRX (k). The Ki67 proliferation index is below 1% (l). Scale bars 200 μm in a for a–l, 25 μm in the inset in a for all insets in a–f
