Fig. 5.
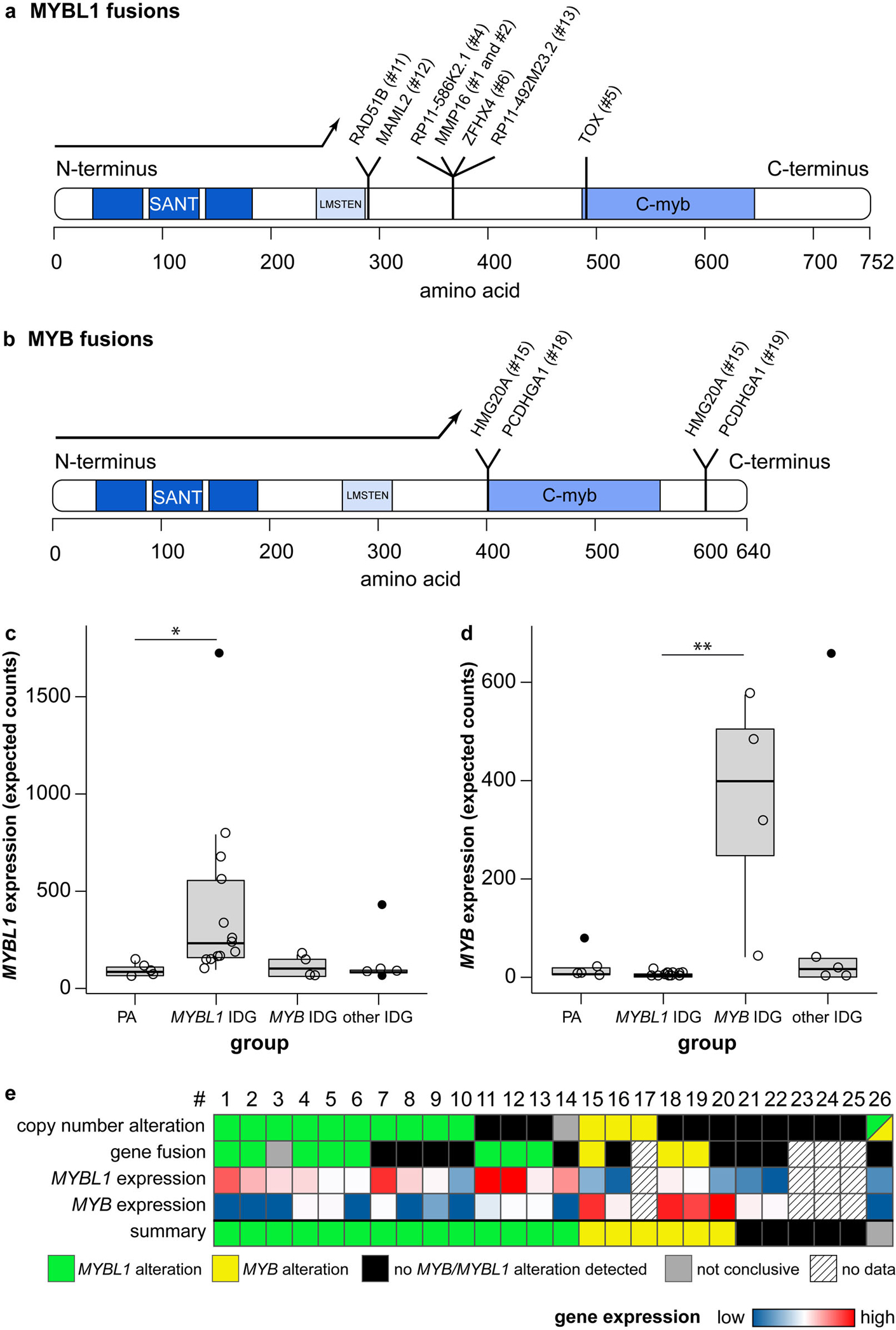
Isomorphic diffuse gliomas have fusions of the MYBL1- and MYB-genes and show a corresponding mRNA-overexpression. a, b Canonical MYBL1- (a) and MYB-protein (b) with loci of fusions to different partners. Protein domains in blue: “SANT” DNA-binding domain, “LMSTEN” transactivating domain, “C-myb” C-terminal negative regulatory domain. Fusions result in a deletion of the C-terminal negative regulatory C-myb domain of MYBL1 (a) or MYB (b), or the 3’ miRNA-binding sites of MYB (not included in depiction as no part of the MYB protein). (c, d) Many isomorphic diffuse gliomas show an overexpression of MYBL1 (c) or MYB (d). Compared were pilocytic astrocytomas (“PA”), isomorphic diffuse gliomas with MYBL1-alterations (“MYBL1 IDG”) or MYB-alterations (“MYB IDG”) in the CNP and/or RNA sequencing, and isomorphic diffuse gliomas without evidence of MYBL1/MYB-alterations (“other IDG”). Outliers are depicted with filled circles. p = 0.022 for PA versus MYBL1 IDG in c, p = 0.009 for MYBL1 versus MYB IDG in d (p-values adjusted for multiple comparisons). (e) Summary of alterations of MYBL1 and MYB in the 26 isomorphic diffuse gliomas of this study detected with different methods. For better differentiation, the range of the colour scale for the MYBL1 expression does not account for the outlier. #: case number
