Figure 4. CysK target confirmation studies.
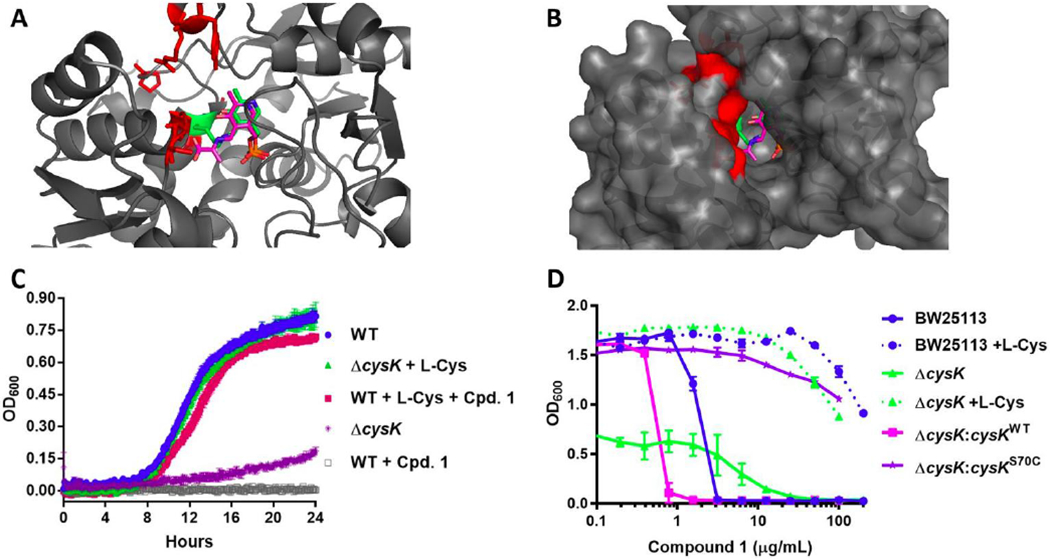
(A) Residues altered by spontaneous mutants induced by compound 1 are highlighted in red on the E. coli CysK structure (PDB 5J43)28. The PLP cofactor is represented in green sticks and the aminoacrylate intermediate from the M. tuberculosis structure (PDB2Q3D) is overlaid in pink sticks. (B) Surface map representation. (C) Survival studies of E. coli BW25113 and ΔcysK in the presence of 16 μg/mL (10x MIC) compound 1 and/or 10 μg/mL L-cysteine. (D) Episomal expression of the cysK gene harboring the spontaneous mutation S70C (Supplementary Table 3) confers resistance to compound 1.
