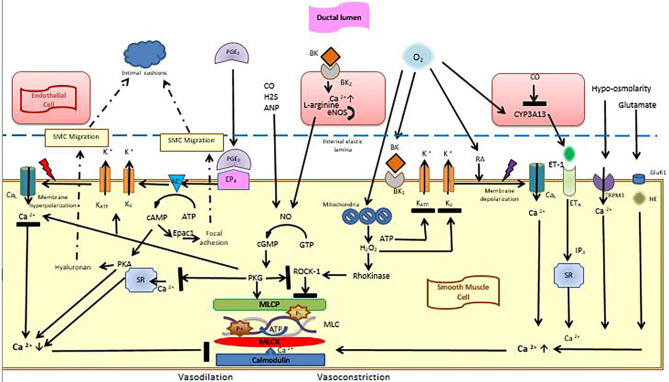
Figure 1.
Vasoconstrictive and vasodilatory effects in the ductal smooth muscle cell. Smooth muscle cells are lined with an internal elastic lamina, on which endothelial cells reşide. Vasodilation is maintained by the interaction of PGE2 with its receptor EP4, which triggers potassium outflow through voltage-sensitive potassium channels, which leads to membrane hyperpolarization. Thereby, calcium entry into the cells decreases and binding of calmodulin to MLCK is inhibited. cAMP and cGMP are also effective during this process. After birth, high oxygen tension, which is sensed through the mitochondria triggers the formation of H2O2 which blocks Rho-kinase pathway as well as potassium channels leading to membrane depolarization and calcium entry into cells. Calcium entry is also stimulated by endothelin-1, hypo-osmolarity and glutamate. Calcium activates MLCK, which leads to MLC phosphorylation and vasoconstriction. cAMP is also effective in smooth muscle migration and intimal cushion formation. AC, adenylyl cyclase; ANP, Atrial Natriuretic peptide; ATP, Adenosine Tri Phosphate; BK, Bradykinin; BK1, Bradykinin receptor; CaL, calcium channels; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; cGMP, cyclic guanosin monophosphate; CO, Carbon monoxide; CYP3A13, cytochrome P450; eNOS, endogenous nitric oxide synthase; EP4, Prostaglandin receptor 4; ET-1, Endothelin-1; ETA, endothelin receptor A; epac, exchange protein activated cAMP; H2, Hydrogen sülfite; GluR1, glutamate receptor-1; KATP, KV, Voltage-dependent potassium channels; NE, Norepinephrine; MLC, Myosin Light Chain; MLCK, Myosin Light Chain Kinase; MLCP, Myosin Light Chain Phosphatase; NO, nitric oxide; PKA, cAMP-dependent protein kinase; PGE2, Prostaglandin E2; PKG, cGMP-dependent protein kinase; RA, Retinoic acid; ROCK-1, Rho-associated protein kinase-1; SR, Sarcoplasmic Reticulum; SMC, Smooth Muscle Cell; TRMP3, transient receptor potential melastatin 3 (Figure courtesy of Fahri Ovali).