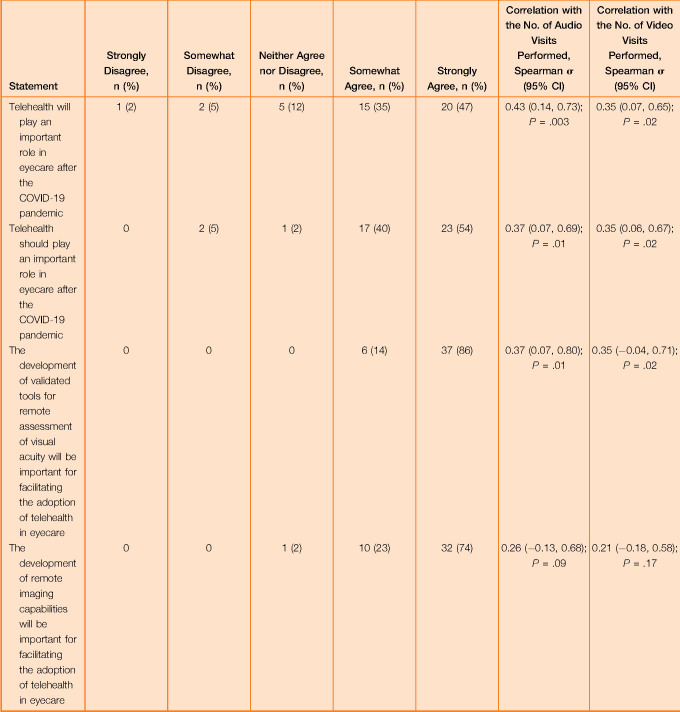
Table 2.
Provider attitudes toward telehealth and correlation with frequency of performing telehealth in the initial survey.
| Statement | Strongly Disagree, n (%) | Somewhat Disagree, n (%) | Neither Agree nor Disagree, n (%) | Somewhat Agree, n (%) | Strongly Agree, n (%) | Correlation with the No. of Audio Visits Performed, Spearman σ (95% CI) | Correlation with the No. of Video Visits Performed, Spearman σ (95% CI) |
| Telehealth will play an important role in eyecare after the COVID-19 pandemic | 1 (2) | 2 (5) | 5 (12) | 15 (35) | 20 (47) | 0.43 (0.14, 0.73); P = .003 | 0.35 (0.07, 0.65); P = .02 |
| Telehealth should play an important role in eyecare after the COVID-19 pandemic | 0 | 2 (5) | 1 (2) | 17 (40) | 23 (54) | 0.37 (0.07, 0.69); P = .01 | 0.35 (0.06, 0.67); P = .02 |
| The development of validated tools for remote assessment of visual acuity will be important for facilitating the adoption of telehealth in eyecare | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 (14) | 37 (86) | 0.37 (0.07, 0.80); P = .01 | 0.35 (−0.04, 0.71); P = .02 |
| The development of remote imaging capabilities will be important for facilitating the adoption of telehealth in eyecare | 0 | 0 | 1 (2) | 10 (23) | 32 (74) | 0.26 (−0.13, 0.68); P = .09 | 0.21 (−0.18, 0.58); P = .17 |