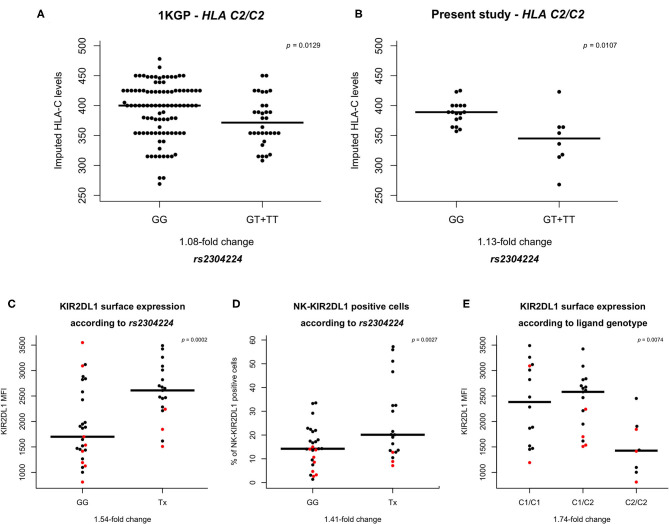
Figure 1.
HLA-C and KIR2DL1 expression are associated with genetic variants. (A,B) rs2304224 in KIR2DL1 marks in silico HLA-C surface expression (28) in two different cohorts. The presence of allele rs2304224*T marks lower HLA-C expression in (A) 130 C2/C2 homozygotes out of 955 individuals from 1000 genomes consortium and (B) 25 C2/C2 homozygotes out of 308 Euro-Brazilians from Curitiba (present study). (C) Higher KIR2DL1 surface expression and (D) increased presence on NK cells are also associated with the variant rs2304224*T (p = 0.0002 and p = 0.0027, respectively). (E) HLA-C genotype is associated to KIR2DL1 surface expression (p = 0.0074). There is no difference in expression, however, between homozygotes C1/C1 and heterozygotes C1/C2 (p = 0.44). Homozygosity for C2/C2, on the other hand, is associated with lower KIR2DL1 surface expression than in C1/C1 (p = 0.0031) and C1/C2 (p = 0.0016). Each dot in the graphs represents one individual. Red dots indicate hemizygosity for KIR2DL1. Median values are shown in horizontal lines and statistical significance is indicated in the top right corners of each plot.