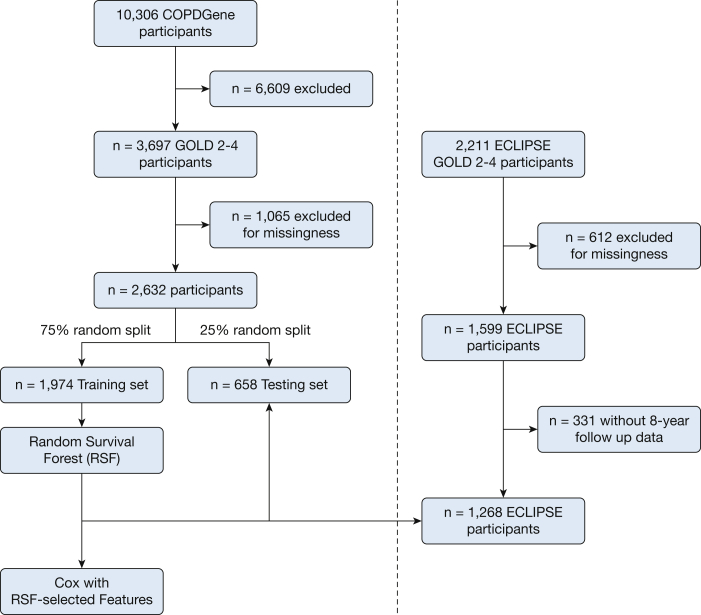
Figure 1.
Schematic of study design. A total of 2,632 participants in COPDGene were randomly split into training (n = 1,974) and testing (n = 658) data sets. A random survival forest algorithm was applied to the training data set, and features chosen by variable importance were used to develop a Cox regression model. Both models were tested in the testing data set of COPDGene and externally in a sample of participants in ECLIPSE (n = 1,268). COPDGene = Genetic Epidemiology of COPD; ECLIPSE = Evaluation of COPD Longitudinally to Identify Predictive Surrogate Endpoints; GOLD = Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease; RSF = random survival forest.