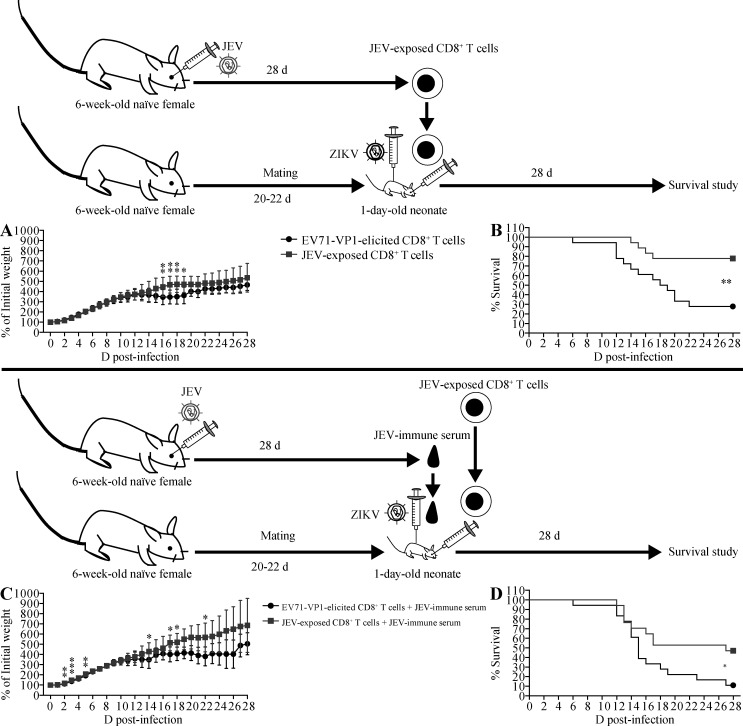
Figure 7.
Transfer of JEV-elicited CD8+ T cells increases the survival of ZIKV-infected mice in the absence or presence of JEV-immune serum. (A and B) 1-d-old naive C57BL/6 mice were r.o. injected with 2 × 106 CD8+ T cells from EV71-VP1–immunized mice (n = 18) or JEV-exposed mice injected r.o. with JEV (102 PFU) 28 d earlier (n = 18). 2 h later, the neonates were injected s.c. with ZIKV (102 FFU). Weights and survival were recorded daily for 28 d. (C and D) Mice were treated as described for A and B except that immediately following infusion of neonatal mice with CD8+ T cells isolated from EV71-VP1–immunized mice (n = 18) or JEV-exposed mice (n = 17), recipient mice were s.c. injected with 3 µl of JEV-immune mouse sera and then s.c. inoculated with ZIKV (102 FFU) 6 h after the infusion of T cells and sera. Data are presented as the mean ± SD and are pooled from two experiments, each with nine mice/group (A and B) or from two experiments, each with 8 or 9 mice per group (C and D). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 by two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test (A and C) or log-rank test (B and D).