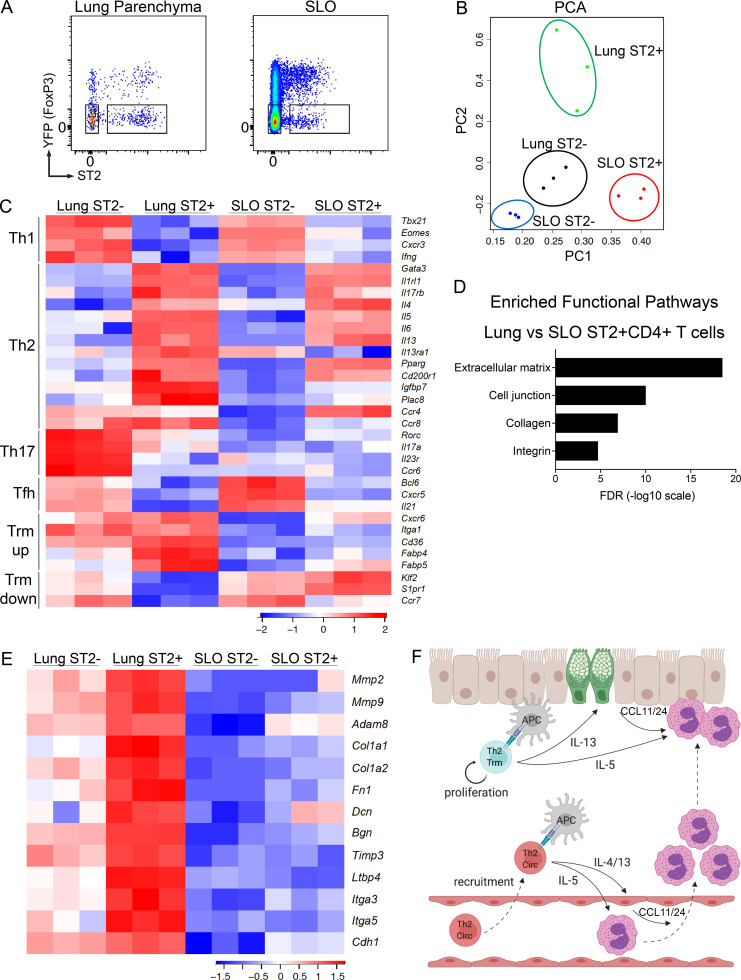
Figure 5.
Shared and distinct transcriptional profiles of Th2 Trm and circulating memory Th2 cells. (A–E) FoxP3YFPCre mice were sensitized and challenged with intranasal HDM and rested for 6 wk followed by lung and LN/spleen (SLO) harvest. (A) Representative flow cytometry of lung and SLO CD4+ T cells indicating YFP and ST2 expression as well as sorting gates for YFP−ST2− and YFP−ST2+ populations. (B) Principal component analysis (PCA) plot based on differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data of indicated memory CD4+ T cell populations. (C) Heatmap of expression values of T cell subset genes, including Th1, Th2, Th17, Tfh, and Trm up-regulated and down-regulated genes. (D) Bar graph of statistical significance (false discovery rate [FDR] by the DAVID tool) of pathway enrichment among genes overexpressed in lung YFP−ST2+CD4+ T cells relative to SLO YFP−ST2+CD4+ T cells. (E) Heatmap of a selected subset of genes known to be involved in ECM biology and cell adhesion. Data are from three independent experiments with five HDM-memory mice pooled for each experiment (cell sort and RNA isolation). (F) Model of memory Th2 cell subsets during allergen rechallenge. Transcriptionally distinct memory Th2 cell subsets include Th2 Trm cells persisting in the lung parenchyma (indicated in blue) and circulating memory Th2 cells in the blood (Th2 Circ; indicated in red). After allergen rechallenge, circulating memory Th2 cells traffic into the lung parenchyma and produce type 2 cytokines, promoting perivascular inflammation, CCL11 and CCL24 production, and eosinophil recruitment. Activation of Th2 Trm cells leads to in situ proliferation and production of type 2 cytokines near the airways, which promotes mucus metaplasia (green epithelial cells), CCL11 and CCL24 production, and eosinophil activation. CCL11 and CCL24 are likely produced from multiple structural and immune cell types following allergen rechallenge. Created with BioRender.com.