Figure 2.
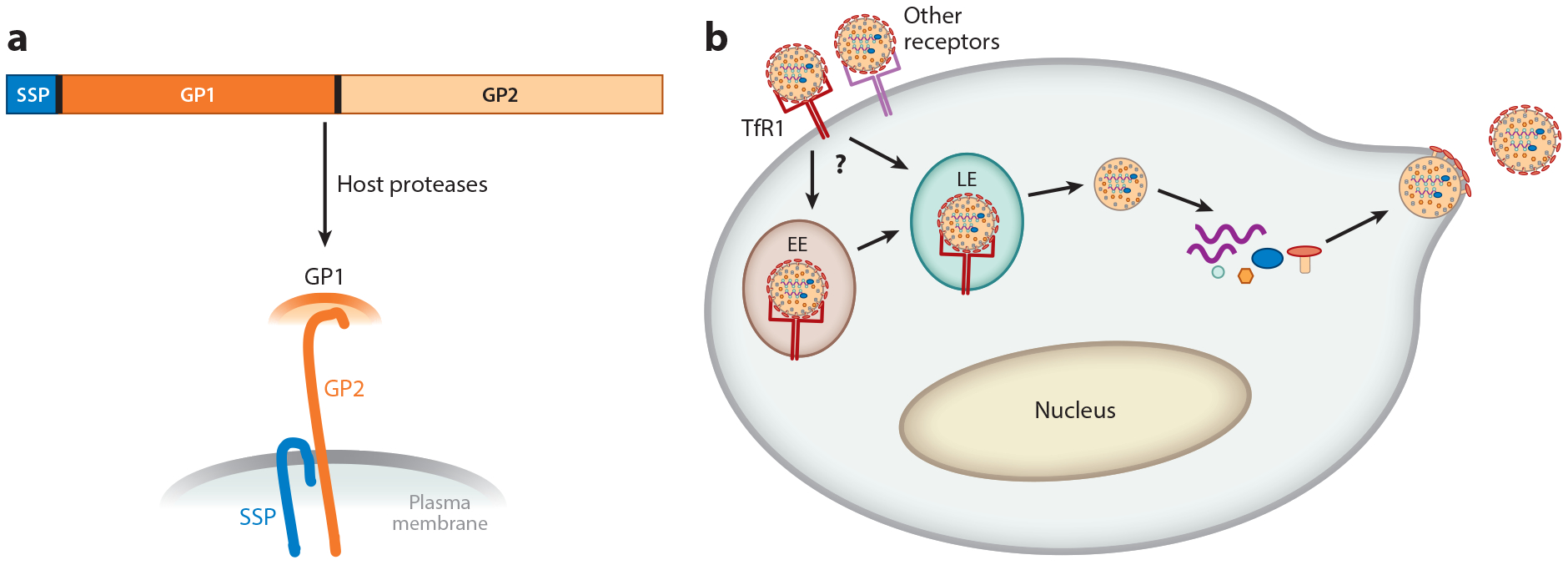
Cellular infection pathway and structure of the arenavirus glycoprotein (GP). (a) The arenavirus glycoprotein precursor (GPC) is translated as a polyprotein, which is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum, modified in the Golgi, and then cleaved by the SK1/S1P cellular protease and host signal peptidase to generate the three subunits—SSP, GP1, and GP2—found in the virion membrane.
(b) The pathogenic New World arenaviruses enter cells after binding to transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1) and perhaps other cell surface molecules. After endocytosis to either the early (EE) or late (LE) acidic endosome, which may be cell type dependent, the viral and host membranes fuse and the capsid is released into the cytoplasm. Transcription of the viral RNA follows, to generate the viral genome as well as mRNAs that encode the viral proteins. After synthesis of the proteins, the viral genomic RNAs are packaged into capsids, and the new viruses bud from the plasma membrane, which already contains the viral GP components.
