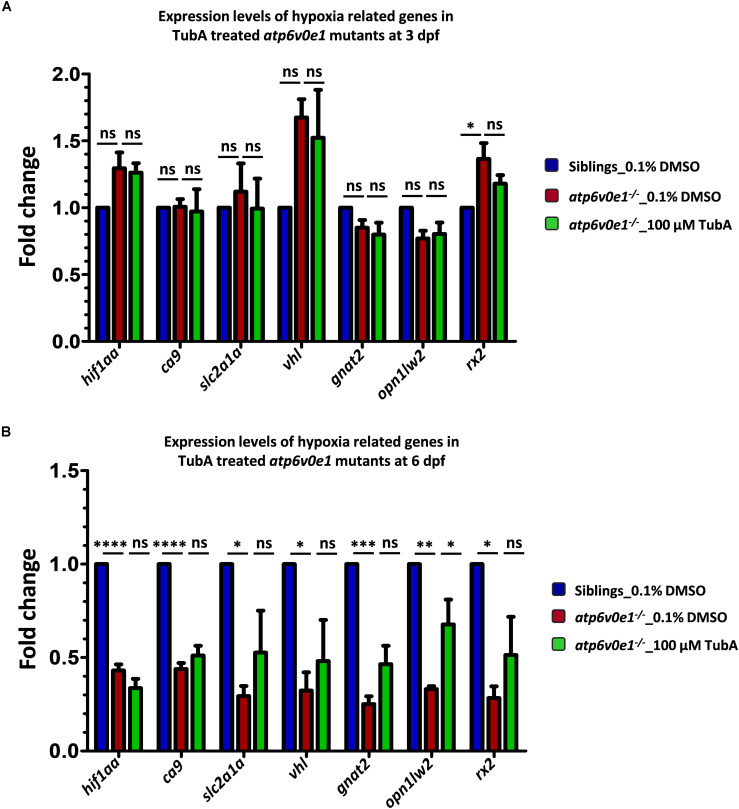
FIGURE 6.
Analysis of hif1aa and targets expression levels in atp6v0e1–/– treated with TubA. (A) hif1aa and select hif1aa downstream target gene(s) expression levels were quantified by qRT-PCR at 4 hpt (i.e., at 3 dpf). No significant changes in hif1aa, slc2a1a, vhl or ca9 transcript levels occurred in atp6v0e1–/– in comparison to vehicle-control treated siblings. Treatment with TubA did not significantly alter these transcript levels either. In atp6v0e1–/–, retinal-specific genes gnat2 and opn1lw2 were not significantly changed but rx2 was significantly upregulated. Upon treatment with TubA, no significant reduction in rx2 transcript levels was detected. (B) Similarly, hif1aa and select hif1aa downstream target gene(s) expression levels were quantified at 3 dpt (i.e., at 6 dpf). A significant reduction in hif1aa, ca9, slc2a1a and vhl transcript levels was identified in vehicle-control treated atp6v0e1–/–. Retinal-specific genes gnat2, opn1lw2 and rx2 were also significantly downregulated compared to vehicle-control treated siblings. TubA-treatment of atp6v0e1–/– resulted in no significant change in hif1aa, ca9, slc2a1a and vhl levels. opn1lw2 transcript levels were significantly increased following TubA-treatment. All experiments were performed in triplicates (n = 60 eyes/treatment condition) and one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons was used for statistical analysis.